HP MSA 1040 HP MSA 1040 SMU Reference Guide (762784-001, March 2014) - Page 130
Configuration View panel, Initiate Replication, Scheduled, Apply
 |
View all HP MSA 1040 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 130 highlights
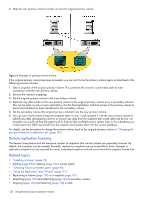
3. Select the link type used between the two systems. 4. If you want to start replication now: a. Select the Initiate Replication and Now options. b. Optionally change the default replication image name. A name is case sensitive; cannot already exist in a vdisk; cannot include a comma, double quote, angle bracket, or backslash; and can have a maximum of 32 bytes. c. Continue with step 7. 5. If you want to schedule replication: a. Select the Initiate Replication and Scheduled options. b. Set the options: • Replication image prefix. Optionally change the default prefix to identify images created by this schedule. The prefix is case sensitive; cannot include a comma, double quote, angle bracket, or backslash; and can have a maximum of 26 bytes. • Replication Mode. Specifies whether to replicate a new snapshot of the volume to the remote system, or to replicate the last (most recent existing) snapshot of the volume to the remote system. • Replication images to Retain. Select the number of replication images to retain for both the primary volume and the secondary volume. When the task runs, the retention count is compared with the number of existing replication images: • Whether the retention count has been reached or not, a new replication image is created. • If the retention count has been reached, the volume's oldest replication image that was created by this schedule and is neither being replicated, nor a current sync point, nor a queued snapshot, is deleted. • If there is more than one queued snapshot, only the oldest queued snapshot is retained. It is retained to serve as the source for the next scheduled replication to create a replication image from. • Start Schedule. Specify a date and a time in the future to be the first instance when the scheduled task will run, and to be the starting point for any specified recurrence. Date must use the format yyyy-mm-dd. Time must use the format hh:mm followed by either AM, PM, or 24H (24-hour clock). For example, 13:00 24H is the same as 1:00 PM. • Recurrence. Specify the interval at which the schedule should run. The default and minimum interval is 30 minutes. • Time Constraint. Specify a time range within which the schedule should run. • Date Constraint. Specify days when the schedule should run. Ensure that this constraint includes the Start Schedule date. • End Schedule. Specify when the schedule should stop running. c. Continue with step 7. 6. If you do not want to start or schedule replication, clear the Initiate Replication checkbox. The replication set will still be created and you can replicate the volume at a later time. 7. Click Apply. Within a couple of minutes, the replication set is created and the following changes occur in the Configuration View panel: • Under the primary vdisk: • The selected primary volume changes to a master volume, and is designated as a Primary Volume. • If the secondary volume is on a remote system, the secondary volume appears under the primary volume. • If a replication was performed, under both the primary volume and the secondary volume a replication image appears. • If not already present, the primary volume's snap pool appears. • Under the secondary vdisk: • The secondary volume appears. • If the primary volume is on a remote system, the primary volume appears under the secondary volume. • If a replication was performed, under both the primary volume and the secondary volume a replication image appears. • If not already present, the secondary volume's snap pool appears. 130 Using Remote Snap to replicate volumes