HP MSA 1040 HP MSA 1040 SMU Reference Guide (762784-001, March 2014) - Page 29
Related topics, About the system date and time, About storage-space color codes, Language, Character
 |
View all HP MSA 1040 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
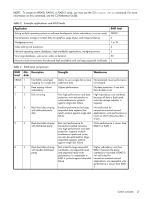
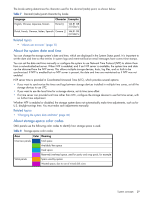
The locale setting determines the character used for the decimal (radix) point, as shown below. Table 7 Decimal (radix) point character by locale Language Character Examples English, Chinese, Japanese, Korean Period (.) 146.81 GB 3.0 Gbit/s Dutch, French, German, Italian, Spanish Comma (,) 146,81 GB 3,0 Gbit/s Related topics • "About user accounts" (page 15) About the system date and time You can change the storage system's date and time, which are displayed in the System Status panel. It is important to set the date and time so that entries in system logs and event-notification email messages have correct time stamps. You can set the date and time manually or configure the system to use Network Time Protocol (NTP) to obtain them from a network-attached server. When NTP is enabled, and if an NTP server is available, the system time and date can be obtained from the NTP server. This allows multiple storage devices, hosts, log files, and so forth to be synchronized. If NTP is enabled but no NTP server is present, the date and time are maintained as if NTP was not enabled. NTP server time is provided in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which provides several options: • If you want to synchronize the times and logs between storage devices installed in multiple time zones, set all the storage devices to use UTC. • If you want to use the local time for a storage device, set its time zone offset. • If a time server can provide local time rather than UTC, configure the storage devices to use that time server, with no further time adjustment. Whether NTP is enabled or disabled, the storage system does not automatically make time adjustments, such as for U.S. daylight savings time. You must make such adjustments manually. Related topics • "Changing the system date and time" (page 46) About storage-space color codes SMU panels use the following color codes to identify how storage space is used. Table 8 Storage-space color codes Area Color Meaning Overview panels Vdisk panels Total space Available/free space Used space Reserved/overhead space, used for parity and snap pools, for example Space used by spares Wasted space, due to use of mixed disk sizes System concepts 29