Dell PowerEdge T140 EMC PowerEdge Servers Troubleshooting Guide - Page 89
Foreign, properties, the Foreign Disks and Global Hot Spares.
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge T140 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 89 highlights
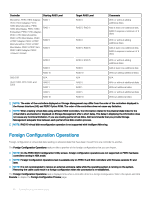
The Foreign Configuration Preview page provides a preview of the foreign disks and enables you to perform operations such as, importing, recovering, or clearing the foreign disks. You can also import or clear a locked foreign configuration. If any foreign configurations that are locked by using Local Key manager (LKM) are detected, the associated Encryption Key Identifier is displayed prompting you to provide the corresponding passphrase to unlock the drives. To avoid unlocking foreign configurations and to proceed to preview, import, or clear a foreign configuration that has not been locked, on the PERC BIOS Configuration Utility Foreign Configuration screen, click Skip or Continue. If you do not want to import or clear the foreign configurations, or in case of loss of the associated passphrase of the corresponding Encryption Key Identifier, execute the Instant Encrypt Erase task for the physical disks. CAUTION: Executing the Instant Encrypt Erase task erases all data on the physical disk. Some conditions, such as an unsupported RAID level or an incomplete disk group, can prevent the import or recovery of foreign virtual disks. Foreign Configuration properties The following table describes the properties that are displayed on the PERC BIOS Configuration Utility Foreign Configuration screen for the Foreign Disks and Global Hot Spares. Table 20. Memory channels Property Status Name State Definition These icons represent the severity or health of the storage component. • -Normal/OK • -Warning/Non-critical • -Critical/Failure/Error Displays the name of the foreign configuration and is available as a link. This link enables you to access the physical disks that constitute the foreign disk. Displays the current state of the foreign configuration. Possible values are: • Ready - The foreign disk can be imported and functions normally after import. • Degraded - The foreign disk is in degraded state and rebuilds after import. • Failed - The foreign disk has encountered a failure and is no longer functioning. You cannot import the foreign configuration. The foreign configuration may be in degraded or failed state due to any of the following reasons: • Missing physical disk - One of the physical disk(s) in the potential virtual disk is missing or not available. • Missing span - One or more spans of a hybrid virtual disk is missing. • Stale physical disks - One or more physical disks in the configuration may contain out-of-date data relating to other disks of that virtual disk. Hence, the data integrity of the imported virtual disk is not intact. • Unsupported configuration of the virtual disk - The virtual disk has an unsupported RAID level. • Import and Export - The virtual disks available for import exceed the number of virtual disks available for export. Troubleshooting hardware issues 89