HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 10
Protection switchover technologies, Technology, Introduction, Reference
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
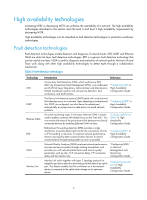
Technology Track Introduction Reference The track module is used to implement collaboration between different modules. The collaboration here involves three parts: the application modules, the track module, and the detection modules. These modules collaborate with one another through collaboration entries. That is, the detection modules trigger the application modules to perform certain operations through the track module. More specifically, the detection modules probe the link status, network performance and so on, and inform the application modules of the detection result through the track module. Once notified of network status changes, the application modules deal with the changes to avoid communication interruption and network performance degradation. "Configuring track" in High Availability Configuration Guide Protection switchover technologies Protection switchover technologies aim at recovering network faults. They back up hardware, link, routing, and service information for switchover in case of network faults, to ensure continuity of network services. Table 3 Protection switchover technologies Technology Ethernet Link Aggregation Smart Link MSTP RRPP GR Introduction Reference Ethernet link aggregation, most often simply called link aggregation, aggregates multiple physical Ethernet links into one logical link to increase link bandwidth beyond the limits of any one single link. This logical link is an aggregate link. It allows for link redundancy because the member physical links can dynamically back up one another. "Configuring Ethernet ink aggregation" in Layer 2-LAN Switching Configuration Guide Smart Link is a feature developed to address the slow convergence issue with STP. It provides link redundancy as well as fast convergence in a dual uplink network, allowing the backup link to take over quickly when the primary link fails. "Configuring Smart Link" in High Availability Configuration Guide As a Layer 2 management protocol, the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) eliminates Layer 2 loops by selectively blocking redundant links in a network, and in the mean time, allows for link redundancy. "Configuring spanning tree" in Layer 2-LAN Switching Configuration Guide The Rapid Ring Protection Protocol (RRPP) is a link layer protocol designed for Ethernet rings. RRPP can prevent broadcast storms caused by data loops when an Ethernet ring is healthy, and rapidly restore the communication paths between the nodes in the event that a link is disconnected on the ring. "Configuring RRPP" in High Availability Configuration Guide Graceful Restart (GR) ensures the continuity of packet forwarding when a protocol, such as BGP, OSPF, IPv6 BGP, or OSPFv3, restarts or during an active/standby switchover process. It needs other devices to implement routing information backup and recovery. Layer 3-IP Routing Configuration Guide/Configuration Guide of the corresponding protocols 3