HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 15
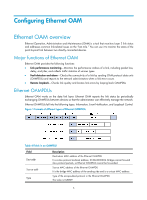
Remote fault detection, Remote loopback, Standards and protocols, Ethernet OAM configuration task list
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
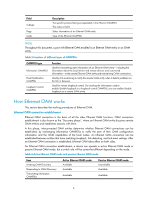
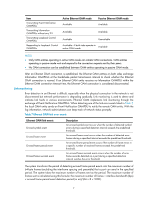
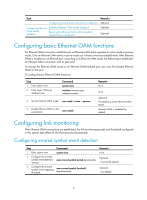
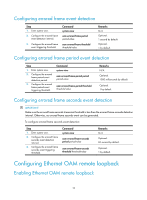
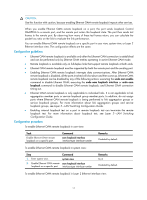
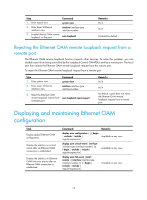
A second in which errored frames appear is called an "errored frame second." Remote fault detection Information OAMPDUs are exchanged periodically among Ethernet OAM entities across established OAM connections. In a network where traffic is interrupted due to device failures or unavailability, the flag field defined in information OAMPDUs allows an Ethernet OAM entity to send error information-the critical link event type-to its peer. You can use the log information to track ongoing link status and troubleshoot problems promptly. Table 8 Critical link events Type Link Fault Dying Gasp Critical Event Description Peer link signal is lost. A power failure or other unexpected error occurred. An undetermined critical event occurred. OAMPDU transmission frequencies Once per second Non-stop Non-stop This Switch Series is able to receive information OAMPDUs carrying the critical link events listed in Table 8. Only the Gigabit fiber ports are able to send information OAMPDUs carrying Link Fault events. This Switch Series is able to send information OAMPDUs carrying Dying Gasp events when the device is rebooted or relevant ports are manually shut down. Physical IRF ports, however, are unable to send this type of OAMPDU. For more information about physical IRF ports, see IRF Configuration Guide. This Switch Series is unable to send information OAMPDUs carrying Critical Events. Remote loopback Remote loopback is available only after the Ethernet OAM connection is established. With remote loopback enabled, the Ethernet OAM entity operating in active Ethernet OAM mode sends non-OAMPDUs to its peer. After receiving these frames, the peer does not forward them according to their destination addresses. Instead, it returns them to the sender along the original path. Remote loopback enables you to check the link status and locate link failures. Performing remote loopback periodically helps to detect network faults promptly. Furthermore, performing remote loopback by network segments helps to locate network faults. Standards and protocols Ethernet OAM is defined in IEEE 802.3ah (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) Access Method and Physical Layer Specifications. Ethernet OAM configuration task list Task Configuring basic Ethernet OAM functions Configuring link monitoring Configuring errored symbol event detection Configuring errored frame event detection Configuring errored frame period event detection Remarks Required Optional Optional Optional 8