HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 206
Static routing-track-NQA collaboration configuration example, Network requirements, Switch
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 206 highlights
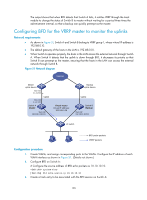
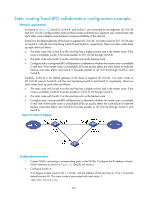
Track Object : 1 State : Negative Pri Reduced : 20 # Display the detailed information about VRRP group 1 on Switch B. display vrrp verbose IPv4 Standby Information: Run Mode : Standard Run Method : Virtual MAC Total number of virtual routers : 1 Interface Vlan-interface2 VRID : 1 Adver Timer : 1 Admin Status : Up State : Master Config Pri : 100 Running Pri : 100 Preempt Mode : Yes Delay Time : 0 Auth Type : None Virtual IP : 192.168.0.10 Virtual MAC : 0000-5e00-0101 Master IP : 192.168.0.102 The output shows that when Switch A detects that the uplink fails through BFD, it decreases its priority by 20 to make sure that Switch B can preempt as the master. Static routing-track-NQA collaboration configuration example Network requirements As shown in Figure 52, Switch A, Switch B, Switch C, and Switch D are connected to two segments 20.1.1.0/24 and 30.1.1.0/24. Configure static routes on these switches so that the two segments can communicate with each other, and configure route backup to improve reliability of the network. Switch A is the default gateway of the hosts in segment 20.1.1.0/24. Two static routes to 30.1.1.0/24 exist on Switch A, with the next hop being Switch B and Switch C, respectively. These two static routes back up each other as follows: • The static route with Switch B as the next hop has a higher priority, and is the master route. If this route is available, Switch A forwards packets to 30.1.1.0/24 through Switch B. • The static route with Switch C as the next hop acts as the backup route. • Configure static routing-track-NQA collaboration to determine whether the master route is available in real time. If the master route is unavailable, the backup route takes effect, and Switch A forwards packets to 30.1.1.0/24 through Switch C. Similarly, Switch D is the default gateway of the hosts in segment 30.1.1.0/24. Two static routes to 20.1.1.0/24 exist on Switch D, with the next hop being Switch B and Switch C, respectively. These two static routes back up each other as follows: • The static route with Switch B as the next hop has a higher priority, and is the master route. If this route is available, Switch D forwards packets to 20.1.1.0/24 through Switch B. • The static route with Switch C as the next hop acts as the backup route. • Configure static routing-track-NQA collaboration to determine whether the master route is available in real time. If the master route is unavailable, the backup route takes effect, and Switch D forwards packets to 20.1.1.0/24 through Switch C. 199