HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 9
High availability technologies, Fault detection technologies
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 9 highlights
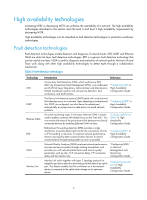
High availability technologies Increasing MTBF or decreasing MTTR can enhance the availability of a network. The high availability technologies described in this section meet the level 2 and level 3 high availability requirements by decreasing MTTR. High availability technologies can be classified as fault detection technologies or protection switchover technologies. Fault detection technologies Fault detection technologies enable detection and diagnosis of network faults. CFD, DLDP, and Ethernet OAM are data link layer fault detection technologies. BFD is a generic fault detection technology that can be used at any layer. NQA is used for diagnosis and evaluation of network quality. Monitor Link and Track work along with other high availability technologies to detect faults through a collaboration mechanism. Table 2 Fault detection technologies Technology CFD DLDP Ethernet OAM BFD NQA Monitor Link Introduction Reference Connectivity Fault Detection (CFD), which conforms to IEEE 802.1ag Connectivity Fault Management (CFM), is an end-to-end per-VLAN link layer Operations, Administration and Maintenance (OAM) mechanism used for link connectivity detection, fault verification, and fault location. "Configuring CFD" in High Availability Configuration Guide The Device link detection protocol (DLDP) deals with unidirectional links that may occur in a network. Upon detecting a unidirectional link, DLDP, as configured, can shut down the related port automatically or prompt users to take actions to avoid network problems. "Configuring DLDP" in High Availability Configuration Guide As a tool monitoring Layer 2 link status, Ethernet OAM is mainly used to address common link-related issues on the "last mile". You can monitor the status of the point-to-point link between two directly connected devices by enabling Ethernet OAM on them. "Configuring Ethernet OAM" in High Availability Configuration Guide Bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) provides a single mechanism to quickly detect and monitor the connectivity of links or IP forwarding in networks. To improve network performance, devices must quickly detect communication failures to restore communication through backup paths as soon as possible. "Configuring BFD" in High Availability Configuration Guide Network Quality Analyzer (NQA) analyzes network performance, services and service quality through sending test packets, and provides you with network performance and service quality parameters such as jitter, TCP connection delay, FTP connection delay and file transfer rate. "Configuring NQA" in Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide Monitor Link works together with Layer 2 topology protocols to adapt the up/down state of a downlink port to the state of an uplink port. This feature enables fast link switchover on a downstream device in response to the uplink state change on its upstream device. "Configuring Monitor Link" in High Availability Configuration Guide 2