HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 184
BFD operating modes, Dynamic BFD parameter changes, Authentication modes, BFD packet format
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 184 highlights
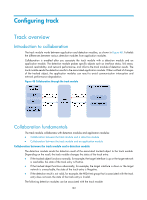
BFD operating modes Before a BFD session is established, BFD has the following operating modes-active and passive. • Active mode-BFD actively sends BFD control packets regardless of whether any BFD control packet is received from the peer. • Passive mode-BFD does not send control packets until a BFD control packet is received from the peer. At least one end must operate in the active mode for a BFD session to be established. After a BFD session is established, both ends must operate in the asynchronous mode-Both endpoints periodically send BFD control packets to each other. BFD considers the session down if it receives no BFD control packets within a specific interval. NOTE: When a BFD session is maintained by sending Echo packets, the session is independent of the operating mode. Dynamic BFD parameter changes After a BFD session is established, both ends can negotiate the related BFD parameters, such as the minimum transmit interval, minimum receive interval, initialization mode, and packet authentication mode. After that, both ends use the negotiated parameters, without affecting the current session state. Authentication modes BFD provides the following authentication methods: • Simple-Simple authentication • MD5-MD5 authentication • SHA1-SHA1 authentication BFD packet format BFD control packets are encapsulated into UDP packets with port number 3784 for single-hop detection or port number 4784 for multi-hop detection. (It can also be 3784 based on the configuration task.) BFD echo packets have a similar format to BFD control packets (except that the Desired Min TX Interval and Required Min RX Interval fields are null), with UDP port number 3785. Figure 47 BFD packet format • Vers-Protocol version. The protocol version is 1. 177