HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 12
Configuring Ethernet OAM, Ethernet OAM overview, Major functions of Ethernet OAM, Ethernet OAMPDUs
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 12 highlights
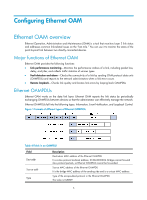
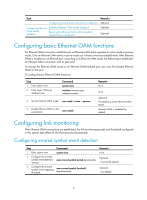
Configuring Ethernet OAM Ethernet OAM overview Ethernet Operation, Administration and Maintenance (OAM) is a tool that monitors Layer 2 link status and addresses common link-related issues on the "last mile." You can use it to monitor the status of the point-to-point link between two directly connected devices. Major functions of Ethernet OAM Ethernet OAM provides the following functions: • Link performance monitoring-Monitors the performance indices of a link, including packet loss, delay, and jitter, and collects traffic statistics of various types • Fault detection and alarm-Checks the connectivity of a link by sending OAM protocol data units (OAMPDUs) and reports to the network administrators when a link error occurs • Remote loopback-Checks link quality and locates link errors by looping back OAMPDUs Ethernet OAMPDUs Ethernet OAM works on the data link layer. Ethernet OAM reports the link status by periodically exchanging OAMPDUs between devices so that the administrator can effectively manage the network. Ethernet OAMPDUs fall into the following types: Information, Event Notification, and Loopback Control. Figure 1 Formats of different types of Ethernet OAMPDUs Table 4 Fields in an OAMPDU Field Dest addr Source addr Type Description Destination MAC address of the Ethernet OAMPDU It is a slow protocol multicast address, 0180c2000002. Bridges cannot forward slow protocol packets, so Ethernet OAMPDUs cannot be forwarded. Source MAC address of the Ethernet OAMPDU It is the bridge MAC address of the sending side and is a unicast MAC address. Type of the encapsulated protocol in the Ethernet OAMPDU The value is 0x8809. 5