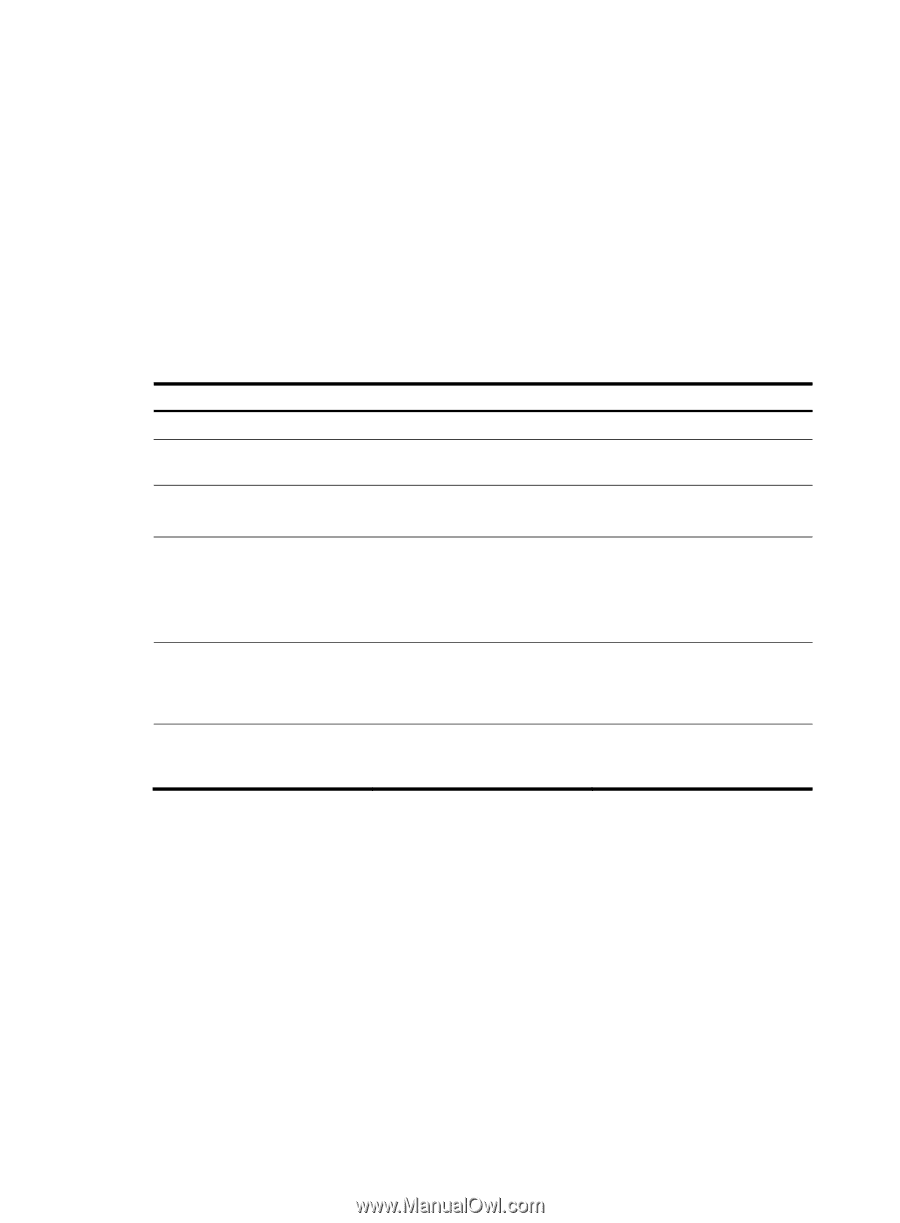
HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 134
Configuration prerequisites, Configuration procedure, Configuring VF tracking, Configuration
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 134 highlights
• If the state of a tracked interface changes from down or removed to up, the priority of the router where the interface resides is automatically restored. • If the state of a track entry changes from negative or invalid to positive, the priority of the router where the track entry is configured is automatically restored. Configuration prerequisites Before you configure router priority, preemptive mode and tracking function, create a VRRP group on an interface and configure a virtual IP address for it. Configuration procedure By configuring router priority, preemptive mode, interface tracking, or a track entry, you can determine which router in the VRRP group serves as the master. To configure router priority, preemptive mode and the tracking function: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view 2. Enter interface view. interface interface-type interface-number 3. Configure router priority in the vrrp vrid virtual-router-id priority VRRP group. priority-value 4. Configure the router in the VRRP group to operate in preemptive mode and configure preemption delay. vrrp vrid virtual-router-id preempt-mode [ timer delay delay-value ] vrrp vrid virtual-router-id track 5. Configure the interface to be interface interface-type tracked. interface-number [ reduced priority-reduced ] 6. Configure VRRP to track a specified track entry. vrrp vrid virtual-router-id track track-entry-number [ reduced priority-reduced | switchover ] Remarks N/A N/A Optional. 100 by default. Optional. The router in the VRRP group operates in preemptive mode and the preemption delay is 0 seconds by default. Optional. No interface is being tracked by default. Optional. Not configured by default. Configuring VF tracking Configuration guidelines • You can configure the VF tracking function when VRRP is operating in either standard protocol mode or load balancing mode. However, the VF tracking function is effective only when VRRP is operating in load balancing mode. • By default, the weight of a VF is 255, and its lower limit of failure is 10. • If the weight of a VF owner is higher than or equal to the lower limit of failure, the priority of the VF owner is always 255 and does not change with the weight value. Therefore, in case of an uplink failure, another VF takes over the VF owner's work and becomes the AVF only when the weight of the VF owner decreases by a properly specified value and becomes lower than the lower limit of failure. In other words, the weight of the VF owner decreases by more than 245. 127