HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 121
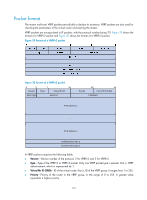
Operation mode, Authentication mode, VRRP timers, VRRP advertisement interval timer
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 121 highlights
VRRP priority is in the range of 0 to 255. The greater the number, the higher the priority. Priorities 1 to 254 are configurable. Priority 0 is reserved for special uses and priority 255 for the IP address owner. When a router acts as the IP address owner, its running priority is always 255. That is, the IP address owner in a VRRP group acts as the master as long as it operates properly. Operation mode A router in a VRRP group operates in either of the following modes: • Non-preemptive mode-When a router in the VRRP group becomes the master, it stays as the master as long as it operates properly, even if a backup is assigned a higher priority later. • Preemptive mode-When a backup finds its priority higher than that of the master, the backup sends VRRP advertisements to start a new master election in the VRRP group and becomes the master. Accordingly, the original master becomes a backup. Authentication mode To avoid attacks from unauthorized users, VRRP adds authentication keys into packets for authentication. VRRP provides the following authentication modes: • simple-Simple text authentication A router sending a packet fills an authentication key into the packet, and the router receiving the packet compares its local authentication key with that of the received packet. If the two authentication keys are the same, the received VRRP packet is considered legitimate. Otherwise, the received packet is considered invalid. • md5-MD5 authentication A router computes the digest of a packet to be sent by using the authentication key and MD5 algorithm and saves the result in the authentication header. The router that receives the packet performs the same operation by using the authentication key and MD5 algorithm, and compares the result with the content in the authentication header. If the results are the same, the router that receives the packet considers the packet an authentic and valid VRRP packet. Otherwise, the router considers the packet invalid. On a secure network, you can choose not to set the authentication mode. VRRP timers VRRP timers include VRRP advertisement interval timer and VRRP preemption delay timer. VRRP advertisement interval timer The master in a VRRP group periodically sends VRRP advertisements to inform the other routers in the VRRP group that it operates properly. You can adjust the interval for sending VRRP advertisements by setting the VRRP advertisement interval timer. If a backup receives no advertisements in a period three times the interval, the backup regards itself as the master and sends VRRP advertisements to start a new master election. VRRP preemption delay timer To avoid frequent state changes among members in a VRRP group and provide the backups enough time to collect information (such as routing information), each backup waits for a period of time (the preemption delay time) after it receives an advertisement with the priority lower than the local priority, then sends VRRP advertisements to start a new master election in the VRRP group and becomes the master. 114