HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 54
Configuring RRPP, RRPP overview, Background, Basic concepts in RRPP, RRPP domain
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 54 highlights
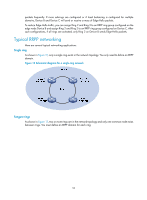
Configuring RRPP RRPP overview The Rapid Ring Protection Protocol (RRPP) is a link layer protocol designed for Ethernet rings. RRPP can prevent broadcast storms caused by data loops when an Ethernet ring is healthy, and rapidly restore the communication paths between the nodes in the event that a link is disconnected on the ring. Background Metropolitan area networks (MANs) and enterprise networks usually use the ring structure to improve reliability. However, services will be interrupted if any node in the ring network fails. A ring network usually uses Resilient Packet Ring (RPR) or Ethernet rings. RPR is high in cost because it needs dedicated hardware. Contrarily, the Ethernet ring technology is more mature and economical, so it is increasingly widely used in MANs and enterprise networks. Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP), and RRPP can eliminate Layer-2 loops. RSTP and MSTP are mature. However, they take several seconds to converge. RRPP is an Ethernet ring-specific data link layer protocol, and it converges faster than RSTP and MSTP. Additionally, the convergence time of RRPP is independent of the number of nodes in the Ethernet ring. RRPP can be applied to large-diameter networks. Basic concepts in RRPP Figure 11 RRPP networking diagram RRPP domain The interconnected devices with the same domain ID and control VLANs constitute an RRPP domain. An RRPP domain contains the following elements-primary ring, subring, control VLAN, master node, transit node, primary port, secondary port, common port, edge port, and so on. As shown in Figure 11, Domain 1 is an RRPP domain, including two RRPP rings: Ring 1 and Ring 2. All the nodes on the two RRPP rings belong to the RRPP domain. 47