HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 122
Packet format,
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 122 highlights
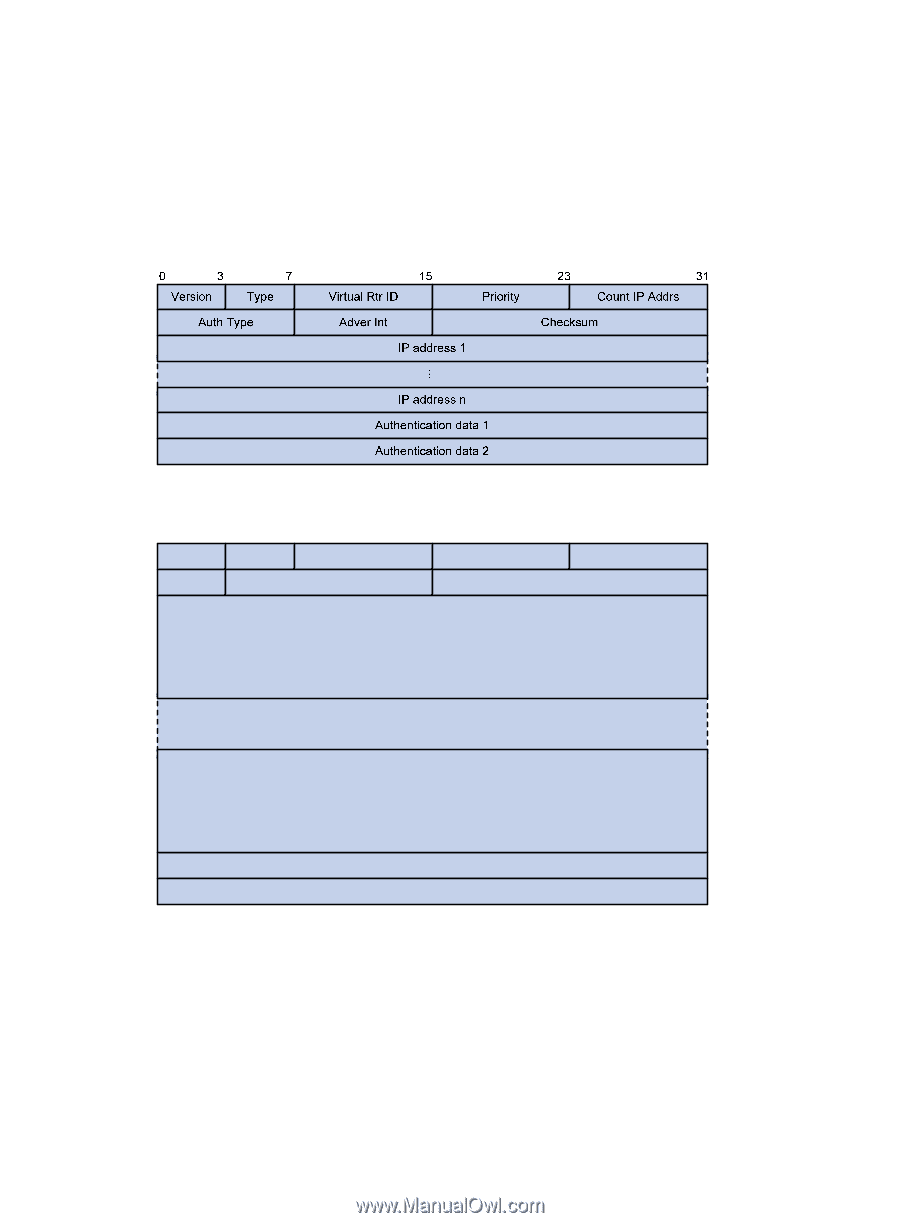
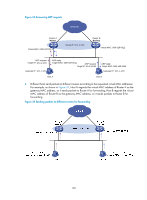
Packet format The master multicasts VRRP packets periodically to declare its existence. VRRP packets are also used for checking the parameters of the virtual router and electing the master. VRRP packets are encapsulated in IP packets, with the protocol number being 112. Figure 29 shows the format of a VRRPv2 packet and Figure 30 shows the format of a VRRPv3 packet. Figure 29 Format of a VRRPv2 packet Figure 30 Format of a VRRPv3 packet 0 3 Version 7 Type 15 Virtual Rtr ID Auth Type Adver Int Priority 23 31 Count IPv6 Addrs Checksum IPv6 address 1 ... IPv6 address n Authentication data 1 Authentication data 2 A VRRP packet comprises the following fields: • Version-Version number of the protocol, 2 for VRRPv2 and 3 for VRRPv3. • Type-Type of the VRRPv2 or VRRPv3 packet. Only one VRRP packet type is present, that is, VRRP advertisement, which is represented by 1. • Virtual Rtr ID (VRID)-ID of the virtual router, that is, ID of the VRRP group. It ranges from 1 to 255. • Priority-Priority of the router in the VRRP group, in the range of 0 to 255. A greater value represents a higher priority. 115