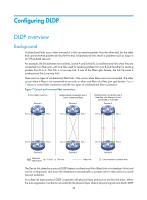
HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches High Availability Configur - Page 39
DLDP processes, A device sends Flush packets when it transits to the Initial state from the Active
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
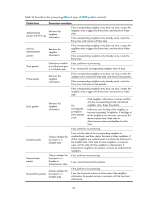
• Non-authentication: { The sending side sets the Authentication field and the Authentication type field of DLDP packets to 0. { The receiving side checks the values of the two fields of received DLDP packets and drops the packets where the two fields conflict with the corresponding local configuration. • Simple authentication: { Before sending a DLDP packet, the sending side sets the Authentication field to the user-configured password and sets the Authentication type field to 1. { The receiving side checks the values of the two fields in received DLDP packets and drops any packets where the two fields conflict with the corresponding local configuration. • MD5 authentication: { Before sending a packet, the sending side encrypts the user configured password using MD5 algorithm, assigns the digest to the Authentication field, and sets the Authentication type field to 2. { The receiving side checks the values of the two fields in received DLDP packets and drops any packets where the two fields conflicting with the corresponding local configuration. DLDP processes 1. On a DLDP-enabled link that is in up state, DLDP sends DLDP packets to the peer device and processes the DLDP packets received from the peer device. DLDP packets sent vary with DLDP states. Table 14 DLDP packet types and DLDP states DLDP state Active Advertisement Probe Disable Type of DLDP packets sent Advertisement packet with RSY tag Normal Advertisement packet Probe packet Disable packet and then RecoverProbe packet NOTE: A device sends Flush packets when it transits to the Initial state from the Active, Advertisement, Probe, or DelayDown state but does not send them when it transits to the Initial state from Inactive or Disable state. 2. A received DLDP packet is processed with the following methods: { In any of the three authentication modes, the packet is dropped if it fails to pass the authentication. { The packet is dropped if the setting of the interval to send Advertisement packets it carries conflicts with the corresponding local setting. { Other processes are as shown in Table 15. 32