HP Z620 HP Remote Graphics Software 5.4.7 - Page 103
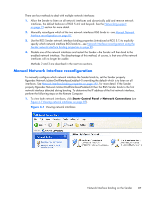
Manual Network Interface reconfiguration, Start> Control Panel > Network Connections
 |
View all HP Z620 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 103 highlights
There are four methods to deal with multiple network interfaces: 1. Allow the Sender to listen on all network interfaces and dynamically add and remove network interfaces, the default behavior of RGS 5.4.0 and beyond. See the Networking support on page 15 section for more detail. 2. Manually reconfigure which of the two network interfaces RGS binds to-see Manual Network Interface reconfiguration on page 87. 3. Use the RGS Sender network interface binding properties (introduced at RGS 5.1) to explicitly specify which network interface RGS binds to-see Network Interface reconfiguration using the Sender network interface binding properties on page 90. 4. Disable one of the network interfaces and restart the Sender-the Sender will then bind to the enabled network interface. The disadvantage of this method, of course, is that one of the network interfaces will no longer be usable. Methods 2 and 3 are described in the next two sections. Manual Network Interface reconfiguration To manually configure which network interface the Sender binds to, set the Sender property Rgsender.Network.IsListenOnAllInterfacesEnabled=0 overriding the default which is to listen on all interfaces. See Network Interface binding properties on page 193, for more detail. If the Sender property Rgsender.Network.IsListenOnAllInterfacesEnabled=0 then the RGS Sender binds to the first network interface detected during booting. To determine the IP address of the first network interface, perform the following steps on the Remote Computer: 1. To view both network interfaces, click Start> Control Panel > Network Connections (see Figure 4-1 Viewing network interfaces on page 87). Figure 4-1 Viewing network interfaces Network Interface binding on the Sender 87