HP Z620 HP Remote Graphics Software 5.4.7 - Page 109
Using RGS, Using RGS in Normal Mode
 |
View all HP Z620 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 109 highlights
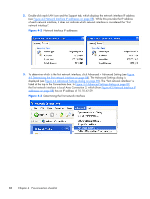
5 Using RGS This chapter describes how to use RGS to establish a connection from a Local Computer to a Remote Computer, including: ● Using RGS in Normal Mode ● Functionality and use of the Receiver Control Panel ● Setup Mode ● Remote Display Window Toolbar ● Remote Computer monitor blanking ● Linux connection considerations ● RGS login methods ● Receiver command line options ● Collaborating Using RGS in Normal Mode Normal Mode is one of the two RGS operating modes-see RGS operating modes on page 25. Normal Mode is the simplest means of establishing a connection-you enter the IP address or hostname of the Remote Computer in the Local Computer Receiver Control Panel, and click Connect. NOTE: The second RGS operating mode, Directory Mode, is described in Using Directory Mode on page 161 . NOTE: The RGS Sender listens on TCP/IP port 42966. The port used by the RGS Receiver is assigned by the Local Computer OS and can vary. Before attempting to connect to a particular Remote Computer for the first time, HP recommends that you verify that the Remote and Local Computers satisfy the Pre-connection checklist on page 84 . The Pre-connection checklist on page 84 can also be used as a troubleshooting aid if a connection attempt fails. After verifying the preconnection checklist, start the Receiver on the Local Computer. This can be done from the start menu or from the command line (see Figure 5-1 Starting the Receiver on Windows on page 93). Figure 5-1 Starting the Receiver on Windows Using RGS in Normal Mode 93