HP Z620 HP Remote Graphics Software 5.4.7 - Page 43
Remote Computer monitor blanking overview, Video overlay surfaces, Image quality - user manual
 |
View all HP Z620 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 43 highlights
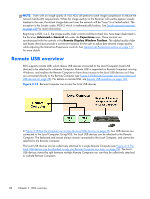
Remote Computer monitor blanking overview New in RGS 5.0, this feature blanks the Remote Computer monitor (if one is connected) when the local user establishes an RGS connection to the Remote Computer and logs in-in other words, becomes the primary user. This feature is provided for security, to ensure that the primary user's desktop session on the Remote Computer is not visible on a monitor connected to the Remote Computer. For details on monitor blanking, see Remote Computer monitor blanking operation on page 99. Video overlay surfaces When the Windows Sender is installed on a computer, video overlay surfaces (also known as overlay planes) are disabled on the computer. Some media players that use video overlay surfaces will not display correctly. This can often be resolved by disabling the use of video overlay surfaces in the media player. Most OpenGL applications will detect the disabling of overlay surfaces, and will work correctly. However, if your OpenGL application attempts to use the disabled overlay surfaces, it may display incorrectly. If this is the case, check to see if your OpenGL application provides a mechanism for the user to manually disable the use of overlay surfaces. Image quality RGS provides high-quality, high-performance image compression and decompression. Image compression is performed on the Remote Computer to reduce the network bandwidth requirements- this enables RGS to be used on standard networks. Image decompression is performed on the Local Computer. RGS supports setting of the Image quality on a per-Receiver basis. Image quality is adjusted using the slide bar in the Remote Display Window Toolbar (see Figure 2-17 Image quality slide bar in the Remote Display Window Toolbar on page 27). As the image quality is increased toward 100, the amount of compression decreases, and the required network bandwidth increases. If a Receiver is supporting multiple Remote Display Windows (see Many-to-one connection on page 17) the slide bar in any Remote Display Window Toolbar can be adjusted-the slide bars in the other Remote Display Windows will automatically track. The Boost checkbox was added beginning with RGS 5.2.6, and requires that both the RGS Sender and Receiver be version 5.2.6 or later. Checking the Boost checkbox will improve (boost) image quality for certain types of images, primarily images containing significant amounts of text or lines. For further information, see Remote Display Window Toolbar on page 98 . Figure 2-17 Image quality slide bar in the Remote Display Window Toolbar Remote Computer monitor blanking overview 27