HP Xw460c HP Integrated Lights-Out 2 User Guide for Firmware 1.75 and 1.77 - Page 174
Using HPQLOMIG, Finding management processors
 |
View all HP Xw460c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 174 highlights
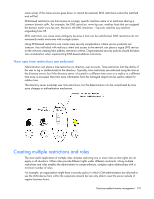
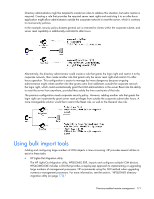
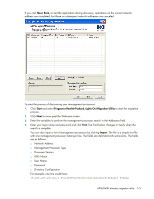
NOTE: The installation utility will present an error message and exit if it detects that the .NET Framework is not installed. Using HPQLOMIG The HPQLOMIG utility automates the process of migrating management processors by creating objects in the directory corresponding to each management processor and associating them to a role. HPQLOMIG has a GUI and provides the user with a wizard approach to implementing or upgrading large amounts of management processors. Finding management processors The first step to migrating is to discover all management processors you want to enable for directory services. You can search for management processors using DNS names, IP addresses, or IP address wildcards. The following rules apply to the variables entered in the Addresses field: • DNS names, IP addresses, and IP address wildcards must be delimited with a semicolon. • The IP address wildcard uses the "*" character in the third and fourth octet fields. For example, IP address 16.100.*.* is valid, whereas IP address 16.*.*.* is not. • Ranges can also be specified using a hyphen. For example, 192.168.0.2-10 is a valid range. A hyphen is only supported in the rightmost octet. • After you click Find, HPQLOMIG begins pinging and connecting to port 443 (the default SSL port). The purpose of these actions is to quickly determine if the target network address is a management processor. If the device does not respond to the ping or connect appropriately on port 443, then it is determined not to be a management processor. HPQLOMIG directory migration utility 174