HP rp3440 User Service Guide, Sixth Edition - HP 9000 rp3410/rp3440 - Page 43
System Power Specifications, Power and Cooling - power consumption
 |
View all HP rp3440 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 43 highlights
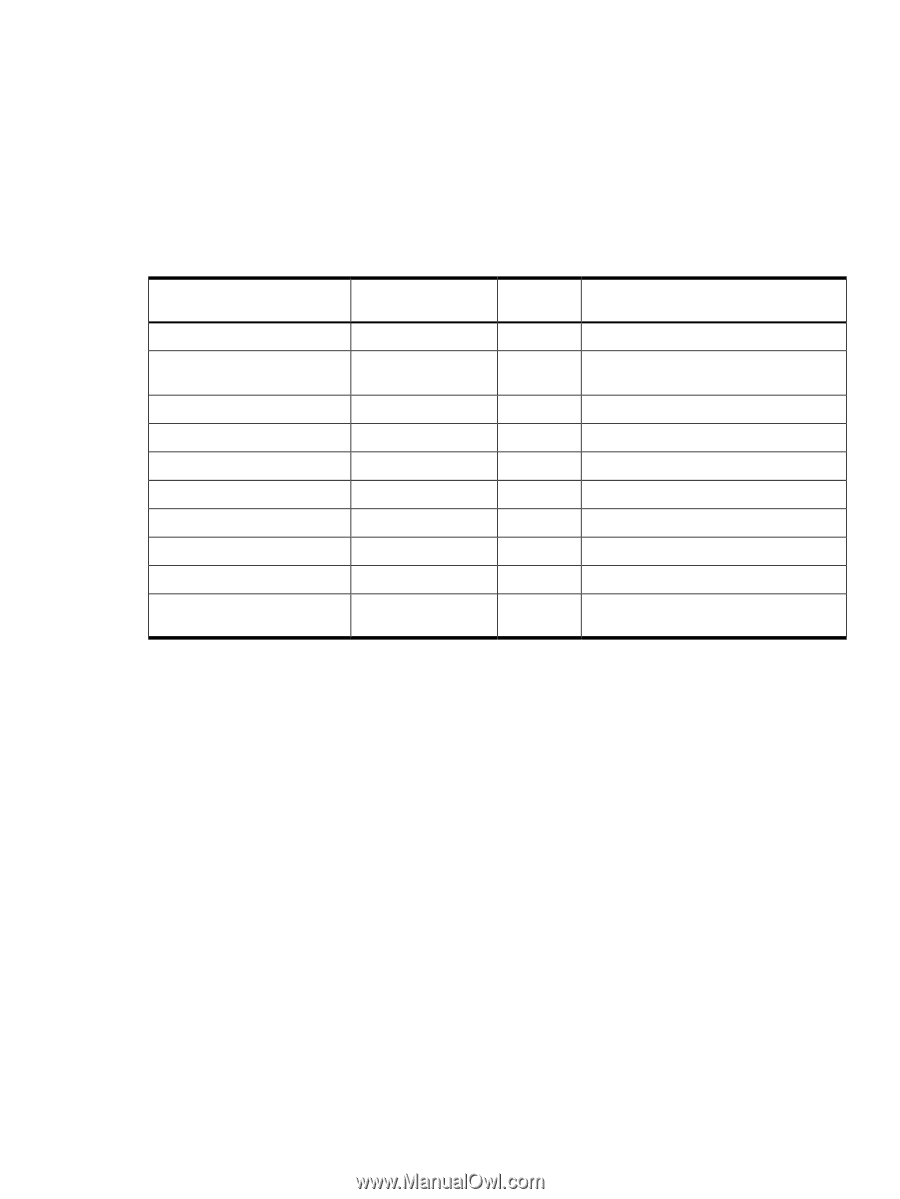
System Power Specifications Available power (output) is the maximum DC power that the power supply can supply to the system. Maximum input power is what the power supply requires from the AC line to deliver the maximum DC output (given worst case efficiency and maximum loading). Maximum input current is the worst case or highest current given the lowest input voltage and the maximum input power. Table 2-4 lists the system power specifications. Table 2-4 System Power Specifications Parameter Input voltage Input current (max) Input frequency Measured input power Available power (output) Maximum current at +12V Maximum current at -12V Maximum current at +3.3V Maximum current at +5V Maximum current at +3.3V standby Total Rating 100 - 240 VAC 7.2A at 115 VAC or 3.6A at 220 VAC 50 to 60 Hz 560W 650W 49A 0.35A 34A 18A 3.5A Peak (15 sec) Off Off Off Off Off 0.5A Off Off 31A Off Max. per PCI-X Sockets 64-bit, 133 MHz Off Off Off Off 85W total for PCI sockets Off 0.1A 4.6A 3A Off If an overload triggers the power supply overload protection, the system is immediately powered off. To reset the power supply unit, follow these steps: 1. Disconnect the power cord. 2. Determine what caused the overload by contacting a HP support representative. 3. Reconnect the power cord. 4. Reboot the system. If an overload occurs twice, there is an undetected short circuit somewhere. When you use the front panel Power button to power off the server, power consumption falls below the low power consumption, but does not reach zero. To reach zero power consumption in "off" mode, either unplug the server or use a power block with a switch. Power and Cooling Typical power consumption for a server is 600W/2050 Btu/h. The power consumptions listed in Table 2-5 are valid for a standard configuration as shipped (one 1 GHz processor, 6 GB of memory, 650W power supply, three hard disk drives, one graphics card, one LVD SCSI card). All information in this section is based on primary power consumptions. Table 2-5 lists additional component power consumption information. Electrical Specifications 43