Netgear GS724Tv4 Software Administration Manual - Page 71
Interface Configuration, To con DHCP snooping interface settings, System, Services
 |
View all Netgear GS724Tv4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 71 highlights
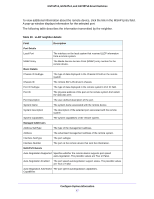
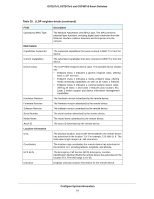
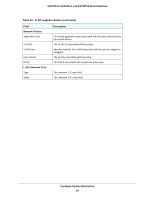
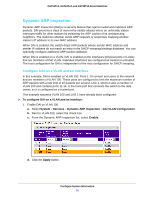
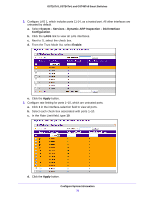
GS716Tv3, GS724Tv4, and GS748Tv5 Smart Switches Interface Configuration Use the DHCP Snooping Interface Configuration screen to view and configure each port as a trusted or untrusted port. Any DHCP responses received on a trusted port are forwarded. If a port is configured as untrusted, any DHCP (or BootP) responses received on that port are discarded. To configure DHCP snooping interface settings: 1. Select System > Services > DHCP Snooping > Interface Configuration. 2. Select one or more ports or LAGs to configure. For information about how to select and configure one or more ports and LAGs, see Configuring Interface Settings on page 28. 3. From the Trust Mode list, select the desired trust mode. • Disabled. The interface is considered to be untrusted and could potentially be used to launch a network attack. DHCP server messages are checked against the bindings database. On untrusted ports, DHCP snooping enforces the following security rules: - DHCP packets from a DHCP server (DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK, DHCPNAK, DHCPRELEASEQUERY) are dropped. - DHCPRELEASE and DHCPDECLINE messages are dropped if the MAC address is in the snooping database but the binding's interface is other than the interface where the message was received. - DHCP packets are dropped when the source MAC address does not match the client hardware address if MAC address validation is globally enabled. • Enabled. The interface is considered to be trusted and forwards DHCP server messages without validation. 4. From the Logging Invalid Packets list, select the packet logging mode. When enabled, the DHCP snooping feature generates a log message when an invalid packet is received and dropped by the interface. 5. In the Rate Limit (pps) field, specify the rate limit value for DHCP snooping purposes. If the incoming rate of DHCP packets exceeds the value of this object for consecutively burst interval seconds, the port will be shut down. If this value is N/A, then the burst interval has no meaning, and rate limiting is disabled. 6. In the Burst Interval (secs) field, specify the burst interval value for rate limiting purposes on this interface. If the rate limit is N/A, then the burst interval has no meaning and the field displays N/A. 7. Click the Apply button. Configure System Information 71