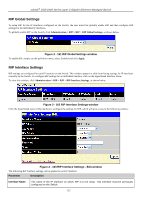
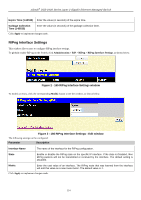
D-Link DGS-3426P Product Manual - Page 146
L2 Features, VLANs, Trunking, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snooping, Loop-back Detection Global Settings
 |
UPC - 790069291982
View all D-Link DGS-3426P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 146 highlights
xStack® DGS-3400 Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch L2 Features VLANs Trunking IGMP Snooping MLD Snooping Loop-back Detection Global Settings Spanning Tree Forwarding & Filtering LLDP Q-in-Q ERPS DULD Settings NLB Multicast FDB Settings Section 3 The following section will aid the user in configuring security functions for the Switch. The Switch includes various functions for VLAN, Trunking, IGMP Snooping, MLD Snooping, Loopback Detection Global Settings, Spanning Tree, Forwarding & Filtering, LLDP and Q-in-Q all discussed in detail in the following section. VLANs VLAN Description A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network topology configured according to a logical scheme rather than the physical layout. VLANs can be used to combine any collection of LAN segments into an autonomous user group that appears as a single LAN. VLANs also logically segment the network into different broadcast domains so that packets are forwarded only between ports within the VLAN. Typically, a VLAN corresponds to a particular subnet, although not necessarily. VLANs can enhance performance by conserving bandwidth, and improve security by limiting traffic to specific domains. A VLAN is a collection of end nodes grouped by logic instead of physical location. End nodes that frequently communicate with each other are assigned to the same VLAN, regardless of where they are physically on the network. Logically, a VLAN can be equated to a broadcast domain, because broadcast packets are forwarded to only members of the VLAN on which the broadcast was initiated. Notes about VLANs on the DGS-3400 Series No matter what basis is used to uniquely identify end nodes and assign these nodes VLAN membership, packets cannot cross VLANs without a network device performing a routing function between the VLANs. The xStack® DGS-3400 Series supports IEEE 802.1Q VLANs and Port-based VLANs. The port untagging function can be used to remove the 802.1Q tag from packet headers to maintain compatibility with devices that are tag-unaware. The Switch's default is to assign all ports to a single 802.1Q VLAN named "default." The "default" VLAN has a VID = 1. The member ports of Port-based VLANs may overlap, if desired. IEEE 802.1Q VLANs Some relevant terms: 137