HP StorageWorks 2/16V Brocade Web Tools Administrator's Guide (53-0000194-01, - Page 112
Admin Domain considerations,
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 2/16V manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 112 highlights
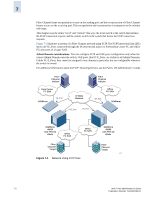
7 Fibre Channel frame encapsulation occurs on the sending port and the reconstruction of Fibre Channel frames occurs on the receiving port. This encapsulation and reconstruction is transparent to the initiator and target. This chapter uses the terms "local" and "remote" this way: the local switch is the switch that initiates the FCIP connection request, and the remote switch is the switch that listens for FCIP connection requests. Figure 7-1 illustrates a portion of a Fibre Channel network using FCIP. The FCIP interswitch link (ISL) shows all VE_Ports connected through the IP network that joins two SANs (Data Center FC and Office FC) into parts of a larger SAN. Admin Domain considerations: You can configure FCIP and GbE ports configuration only when the current Admin Domain owns the switch. GbE ports, like FC E_Ports, are visible in all Admin Domains. Unlike FC E_Ports, they cannot be assigned to any domain in particular, but are configurable wherever the switch is owned. For additional information about the FCIP Tunneling Service, see the Fabric OS Administrator's Guide. Fibre Channel initiator Data Center FC SAN SilkWorm VE_Port Fibre Channel initiator IP WAN Network Office FC SAN VE_Port SilkWorm VE_Port VE_Port SilkWorm 48000 with FR4-18i Blade Office FC SAN Office FC SAN Fibre Channel Target Figure 7-1 Network Using FCIP ISLs SilkWorm 48000 with FR4-18i Blade Fibre Channel Target 31.5 7-2 Web Tools Administrator's Guide Publication Number: 53-0000194-01