HP Visualize J5000 hp Visualize J5000, J7000 workstations service handbook (a4 - Page 163
Displaying and Setting Paths, Table 5-1. System Paths, Table 5-2. Mnemonic Style Notation
 |
View all HP Visualize J5000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 163 highlights
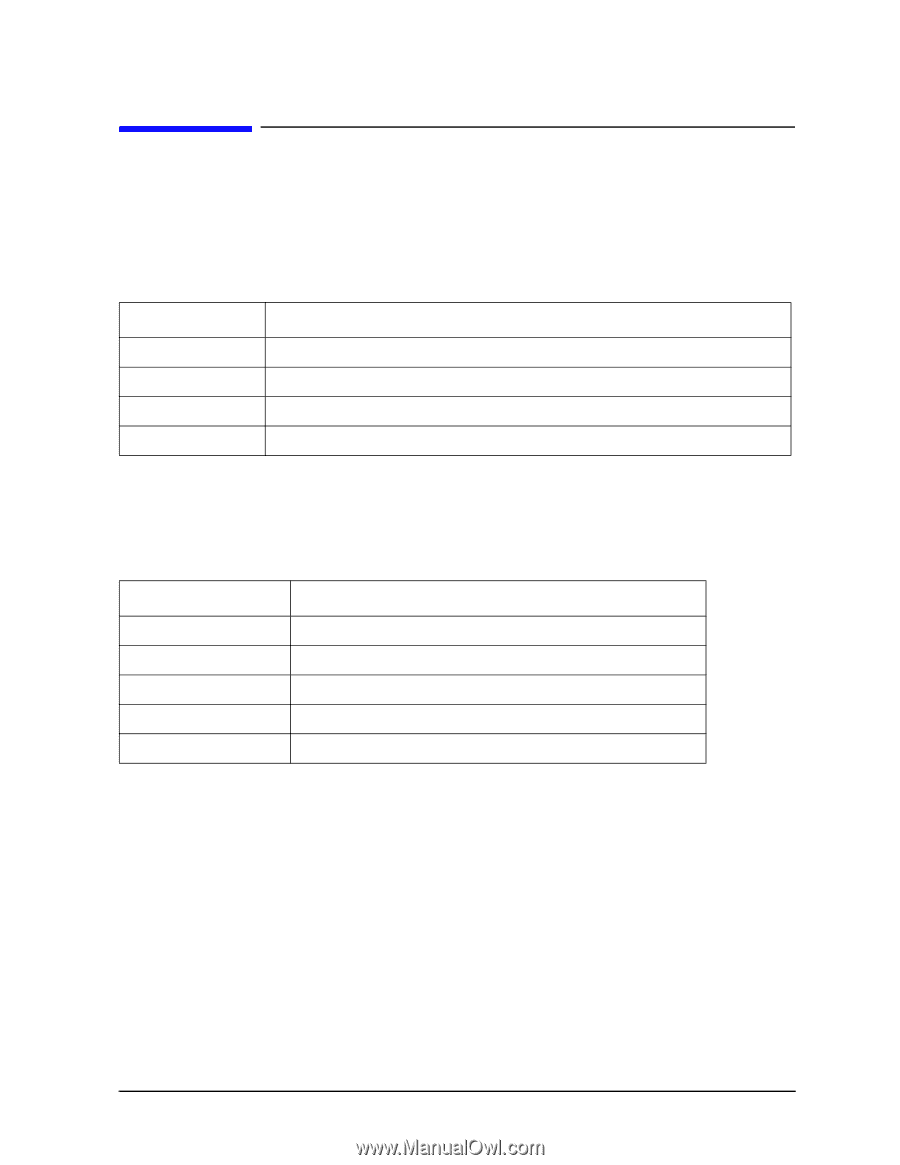
Boot Console Handler Displaying and Setting Paths Displaying and Setting Paths A path is the hardware address of a device that is attached to the I/O system of a workstation. The path command sets the system paths shown in Table 5-1. The path command sets and displays the hardware address of a specified device attached to the I/O bus of the workstation. Table 5-1. System Paths Path Type Device primary or pri The workstation's default boot device (usually the root disk) alternate or alt The workstation's alternate boot device (usually a DDS-format tape device) console or con The workstation's primary display device keyboard or key The workstation's primary ASCII input device To display the current settings for the system paths, type the following at the prompt: Main Menu: Enter command > path [Enter] The paths are displayed in Mnemonic Style Notation, as shown in Table 5-2. Table 5-2. Mnemonic Style Notation I/O Type Built-in LVD SCSI Built-in NSE SCSI Built-in LAN Optional SCSI Built-in IDE Specification Format fwscsi.scsi_address.logical_unit_number scsi.scsi_address.logical_unit_number lan.server_address.init_timeout.io_timeout pcin.scsi_address.logical_unit_number IDE To display the current setting for a particular system path, follow the directions in "Accessing the Boot Console Handler" on page 150, and then type the following at the prompt: Main Menu: Enter command > path path_type [Enter] where path_type is one of the path types listed in Table 5-1. For example, to get the path to the primary boot device, follow the directions in "Accessing the Boot Console Handler" on page 150, and then type the following at the prompt: Main Menu: Enter command > path primary [Enter] Chapter 5 159