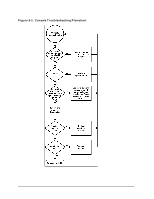
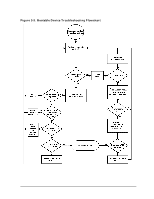
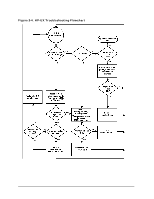
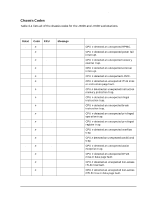
HP Visualize J5000 hp Visualize J5000, J7000 workstations service handbook (a4 - Page 55
Dealing with a Boot Failure, Bootable Media.
 |
View all HP Visualize J5000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
Troubleshooting Dealing with a Boot Failure Dealing with a Boot Failure To start this workstation from an operating system stored on a device different from the usual boot device, to boot from a different disk, or to boot from another type of device (such as an alternate hard disk or CD), see the following situations and examples that use the Boot Console Handler. To access the Boot Console Handler, and for details on using it, see Chapter 5 of this handbook. • To boot from a known device containing a bootable operating system, type the following at the prompt: Main Menu: Enter command > boot device [Enter] where device is the hardware path to the device, specified in Mnemonic Style Notation. For example, to boot an operating system stored on a DDS-format tape in a drive located at scsi.1.0, go to the Main Menu of the Boot Console Handler and then type the following command at the prompt: Main Menu: Enter command > boot scsi.1.0 [Enter] The operating system on the specified device is used to start the workstation. • To interact with the Initial System Loader (ISL) before booting the workstation, type the following at the prompt: Main Menu: Enter command > boot device [Enter] You are prompted: Interact with ISL (Y or N) > y [Enter] Answering yes (y) causes the ISL to be loaded from the specified device. After a short time, the following prompt appears on the screen: ISL> ISL is the program that actually controls the loading of the operating system. By interacting with ISL, you can choose to load an alternate version of the HP-UX operating system. For example, if the usual kernel (/stand/vmunix) on the root disk has become corrupted, boot the workstation from the backup kernel (/stand/vmunix.prev) by typing the following at the ISL> prompt: ISL> hpux /stand/vmunix.prev [Enter] • To find the location of the bootable operating systems on the various media in the file system, use the search ipl command. See the next subsection, "Searching for Bootable Media." Chapter 3 51