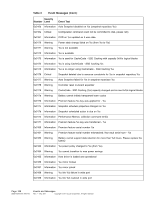
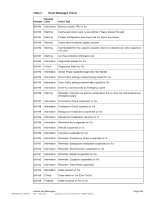
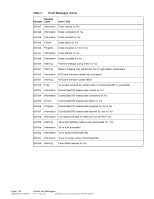
ASRock Z87 Extreme11/ac LSI Mega RAID Storage Manager Guide - Page 172
Glossary
 |
View all ASRock Z87 Extreme11/ac manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 172 highlights
Glossary access policy - A virtual drive property indicating what kind of access is allowed for a particular virtual drive. The possible values are Read/Write, Read Only, or Blocked. alarm enabled - A controller property that indicates whether the controller's onboard alarm is enabled. alarm present - A controller property that indicates whether the controller has an onboard alarm. If present and enabled, the alarm is sounded for certain error conditions. array - See drive group. BBU present - A controller property that indicates whether the controller has an onboard battery backup unit to provide power in case of a power failure. BGI rate - A controller property indicating the rate at which the background initialization of virtual drives will be carried out. BIOS - Basic Input/Output System. The computer BIOS is stored on a flash memory chip. The BIOS controls communications between the microprocessor and peripheral devices, such as the keyboard and the video controller, and miscellaneous functions, such as system messages. cache - Fast memory that holds recently accessed data. Use of cache memory speeds subsequent access to the same data. When data is read from or written to main memory, a copy is also saved in cache memory with the associated main memory address. The cache memory software monitors the addresses of subsequent reads to see if the required data is already stored in cache memory. If it is already in cache memory (a cache hit), it is read from cache memory immediately and the main memory read is aborted (or not started). If the data is not cached (a cache miss), it is fetched from main memory and saved in cache memory. cache flush interval - A controller property that indicates how often the data cache is flushed. caching - The process of using a high speed memory buffer to speed up a computer system's overall read/write performance. The cache can be accessed at a higher speed than a drive subsystem. To improve read performance, the cache usually contains the most recently accessed data, as well as data from adjacent drive sectors. To improve write performance, the cache may temporarily store data in accordance with its write back policies. capacity - A property that indicates the amount of storage space on a drive or virtual drive. coerced capacity - A drive property indicating the capacity to which a drive has been coerced (forced) to make it compatible with other drives that are nominally the same capacity. For example, a 4 Gbyte drive from one manufacturer may be 4,196 Mbytes, and a 4 Gbyte from another manufacturer may be 4,128 Mbytes. These drives could be coerced to a usable capacity of 4,088 Mbytes each for use in a drive group in a storage configuration. coercion mode - A controller property indicating the capacity to which drives of nominally identical capacity are coerced (forced) to make them usable in a storage configuration. consistency check - An operation that verifies that all stripes in a virtual drive with a redundant RAID level are consistent and that automatically fixes any errors. For RAID 1 drive groups, this operation verifies correct mirrored data for each stripe. Page 172 DB09-000202-05 37857-02 Glossary Rev. F - May 2011 Copyright © 2011 by LSI Corporation. All rights reserved.