D-Link DWC-1000 User Manual - Page 185
Dynamic Routing RIP
 |
View all D-Link DWC-1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 185 highlights
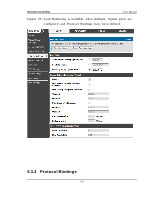
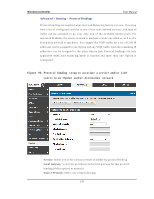
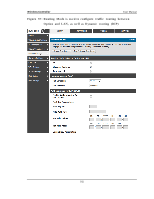
Wireless Controller 6.4.2 Dynamic Routing (RIP) User Manual Th e fo llo win g feat u re is av ailab le u p o n licen s ed act iv at io n o f VPN / Firewall feat u res fo r t h e s y s t em. Setup > Internet Settings > Routing Mode Dy n amic ro u t in g u s in g t h e Ro u t in g In fo rmat io n Pro t o co l (RIP) is an In t erio r Gat eway Pro t o co l (IGP) t h at is co mmo n in LA Ns . W it h RIP t h is co n t ro ller can exch an g e ro u t in g in fo rmat io n wit h o t h er s u ppo rted co nt rollers in t h e LA N an d allo w fo r d y n amic ad ju s tmen t o f ro u t in g t ab les in o rd er t o ad ap t t o mo d ificat io n s in t h e LA N wit h o u t in t erru p t in g t raffic flo w. The RIP direction will define how this controller s ends and receives RIP packets . Choos e between: Both: The controller both broadcas ts its routing table and als o proces s es RIP in fo rmat io n receiv ed fro m o t h er co n t ro llers . Th is is t h e reco mmen d ed s etting in order to fu lly utilize RIP capabilities . Out Only: The controller broadcasts its routing table periodically but does n o t accep t RIP in fo rmat io n fro m o t h er co n t ro llers . In Onl y: Th e co n t ro ller accep t s RIP in fo rmat io n fro m o t h er co n t ro ller, b u t does not broadcas t its routing table. None: The controller neither broadcasts its route table nor does it accept any RIP packets from other controllers . This effectively dis ables RIP. The RIP vers ion is dependent on the RIP s upport of other routing d ev ices in t h e LA N. Di s abl ed: Th is is t h e s et t in g wh en RIP is d is ab led . RIP-1 is a clas s -b ased ro u tin g v ersio n t h at d o es n o t in clu de s ub net in fo rmat io n. This is t h e mo s t co mmo n ly s u p p o rt ed v ers io n . RIP-2 in clu d es all t h e fu n ct io n alit y o f RIPv 1 p lu s it s u p p o rt s s u b n et in fo rmat io n . Th o u g h t h e d at a is s en t in RIP -2 fo rmat fo r b o t h RIP-2B an d RIP-2M , t h e mo d e in which packets are s ent is different. RIP-2B broadcas ts data in the entire s ubnet wh ile RIP-2M s en d s d at a t o mu lt icas t ad d res s es . 183