ZyXEL ENC User Guide - Page 150
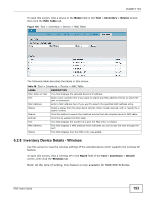
Inventory Device Details - ARP, Table 55, LABEL, DESCRIPTION
 |
View all ZyXEL ENC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 150 highlights
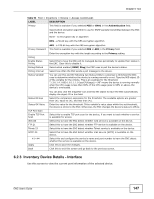
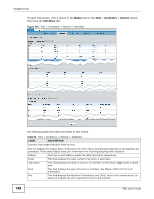
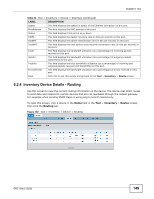
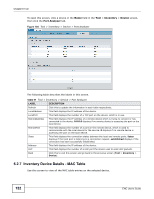
Chapter 6 Tool The following table describes the labels in this screen. Table 55 Tool > Inventory > Device > Routing LABEL DESCRIPTION Refresh Click this to update the information in the table below. Dest This field displays the IP network address of the final destination. Routing is always based on network number. If you need to specify a route to a single host, use a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255 in the subnet mask field to force the network number to be identical to the host ID. Index This field displays the index number of the route. Click a number to edit the static route entry. Metric1 This field displays the primary routing metric which indicates the cost of transmission for routing purposes. IP routing uses hop count as the measurement of cost, 1 displays if the final destination is a direct-connected network or device. -1 displays if this metric is not used. Metric2~4 These fields display the alternative routing metrics for the route. -1 displays if this metric is not used. NextHop This field displays the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is an immediate neighbor of the device, that will forward the packets to the destination. Type This field displays the type of route the device supports. See ipRouteType in RFC1213 for more information. Proto This field displays local if the route is added to the table manually. Otherwise, the field displays a particular routing protocol via which this route was learned. Age This field displays the remaining time (in seconds) before the route is removed from this table (for dynamic routes). 0 means the route does not age out (for static routes). Mask This field displays the subnet mask for this destination. Metric5 This field displays the alternative routing metric for the route. -1 displays if this metric is not used. Info This field displays additional information for the routing protocol shown in the Proto field above. 0.0 means no additional information. Back Click this to exit this screen and go back to the Tool > Inventory > Device screen. 6.2.5 Inventory Device Details - ARP Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to a physical machine address, also known as a Media Access Control or MAC address, on the local area network. Use this screen to view current IP-to-MAC address mapping(s) on the device. 150 ENC User's Guide