Cisco N7K-C7010 Configuration Guide - Page 33
Default UDLD Configuration, UDLD Aggressive and Nonaggressive Modes, Feature, Default Value
 |
UPC - 882658174445
View all Cisco N7K-C7010 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
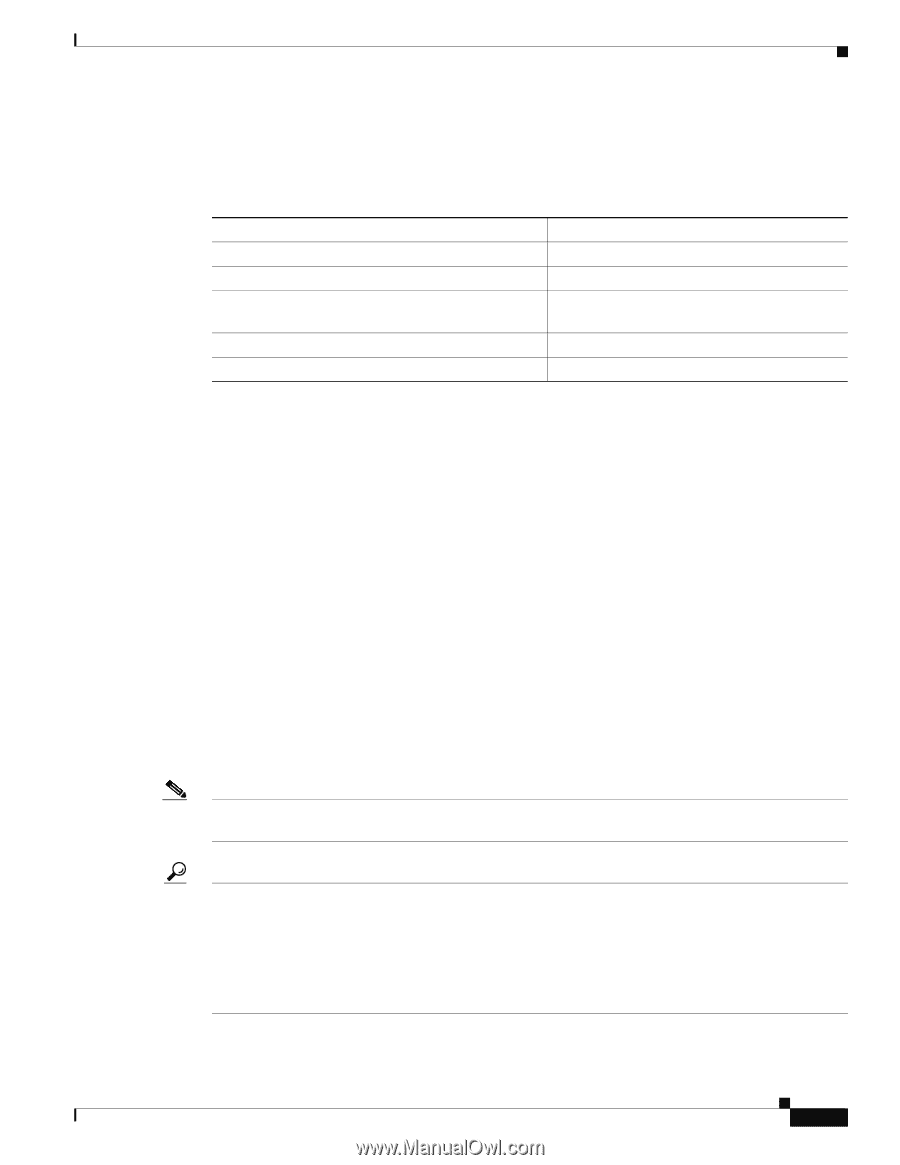
Chapter 2 Configuring Basic Interface Parameters Information About the Basic Interface Parameters Send document comments to [email protected] Default UDLD Configuration Table 2-4 shows the default UDLD configuration. Table 2-4 UDLD Default Configuration Feature UDLD global enable state UDLD per-port enable state for fiber-optic media UDLD per-port enable state for twisted-pair (copper) media UDLD aggressive mode UDLD message interval Default Value Globally disabled Enabled on all Ethernet fiber-optic LAN ports Disabled on all Ethernet 10/100 and 1000BASE-TX LAN ports Disabled 15 seconds For information on configuring the UDLD for the device and its port, see the "Configuring the UDLD Mode" section on page 2-39. UDLD Aggressive and Nonaggressive Modes UDLD aggressive mode is disabled by default. You can configure UDLD aggressive mode only on point-to-point links between network devices that support UDLD aggressive mode. If UDLD aggressive mode is enabled, when a port on a bidirectional link that has a UDLD neighbor relationship established stops receiving UDLD frame, UDLD tries to reestablish the connection with the neighbor. After eight failed retries, the port is disabled. To prevent spanning tree loops, nonaggressive UDLD with the default interval of 15 seconds is fast enough to shut down a unidirectional link before a blocking port transitions to the forwarding state (with default spanning tree parameters). When you enable the UDLD aggressive mode, the following occurs: • One side of a link has a port stuck (both transmission and receive) • One side of a link remains up while the other side of the link is down In these cases, the UDLD aggressive mode disables one of the ports on the link, which prevents traffic from being discarded. Note You enable the UDLD aggressive mode globally to enable that mode on all the fiber ports. You must enable the UDLD aggressive mode on copper ports on specified interfaces. Tip When a line card upgrade is being performed during an in-service software upgrade (ISSU) and some of the ports on the line card are members of a Layer 2 port channel and are configured with UDLD aggressive mode. If one of the remote ports is shutdown, UDLD puts the corresponding port on the local device into error disabled state. This is correct behavior. To restore service after the ISSU has completed, run a shutdown followed by a no shutdown command on the local port. OL-23435-03 Cisco Nexus 7000 Series NX-OS Interfaces Configuration Guide, Release 5.x 2-9