Cisco N7K-C7010 Configuration Guide - Page 87
Access VLANs, Header Without and With 802.1Q Tag
 |
UPC - 882658174445
View all Cisco N7K-C7010 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 87 highlights
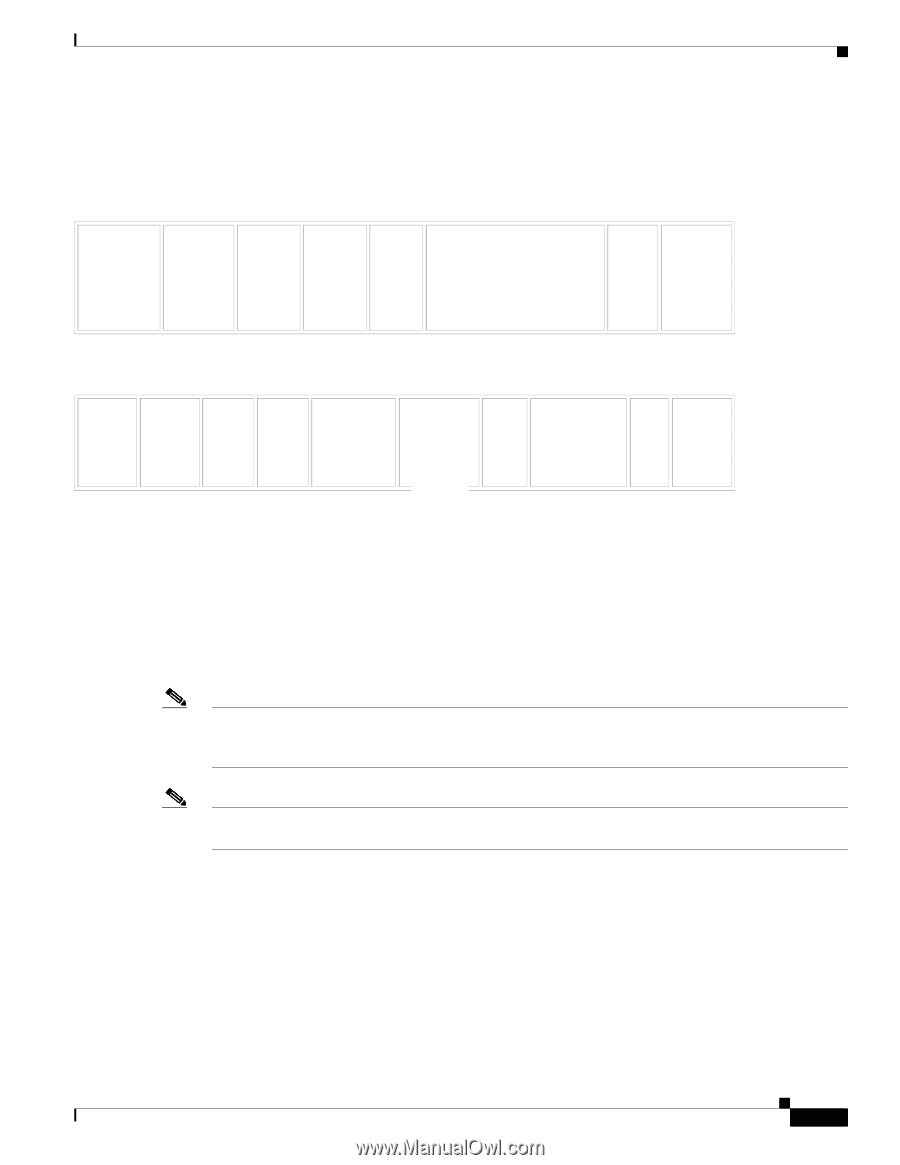
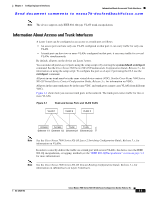
Chapter 3 Configuring Layer 2 Interfaces Information About Access and Trunk Interfaces Send document comments to [email protected] method allows packets that are encapsulated for several different VLANs to traverse the same port and maintain traffic separation between the VLANs. Also, the encapsulated VLAN tag allows the trunk to move traffic end-to-end through the network on the same VLAN. Figure 3-2 Header Without and With 802.1Q Tag Preamble (7 - bytes) Start Frame Delimiter (1 - byte) Dest. MAC Address (6 bytes) Source MAC Address (6 bytes) Length / Type (2 bytes) MAC Client Data (0 - n bytes) Pad (0 - p bytes) Frame Check Sequence (4 - bytes) Preamble (7-bytes) Start Frame Delimiter (1-byte) Dest. Source MAC MAC Address Address (6-bytes) (6-bytes) Length/Type = 802.1Q Tag Type (2-byte) Tag Control Information (2 -bytes) Length /Type (2bytes) MAC Client Data (0-n bytes) Frame Pad Check (0-p Sequence bytes) (4-bytes) 182779 3 bits = User Priority field 1 bit = Canonical Format Identifier (CFI) 12 bits - VLAN Identifier (VLAN ID) Access VLANs Note If you assign an access VLAN that is also a primary VLAN for a private VLAN, all access ports with that access VLAN will also receive all the broadcast traffic for the primary VLAN in the private VLAN mode. Note See the Cisco Nexus 7000 Series NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide, Release 5.x, for complete information on private VLANs. When you configure a port in access mode, you can specify which VLAN will carry the traffic for that interface. If you do not configure the VLAN for a port in access mode, or an access port, the interface carries traffic for the default VLAN (VLAN1). You can change the access port membership in a VLAN by specifying the new VLAN. You must create the VLAN before you can assign it as an access VLAN for an access port. If you change the access VLAN on an access port to a VLAN that is not yet created, the system shuts that access port down. If an access port receives a packet with an 802.1Q tag in the header other than the access VLAN value, that port drops the packet without learning its MAC source address. OL-23435-03 Cisco Nexus 7000 Series NX-OS Interfaces Configuration Guide, Release 5.x 3-5