Cisco MDS-9124 Troubleshooting Guide - Page 423
CLI Commands Used to Access Performance Data, Understanding TCP Parameters for iSCSI
 |
View all Cisco MDS-9124 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 423 highlights
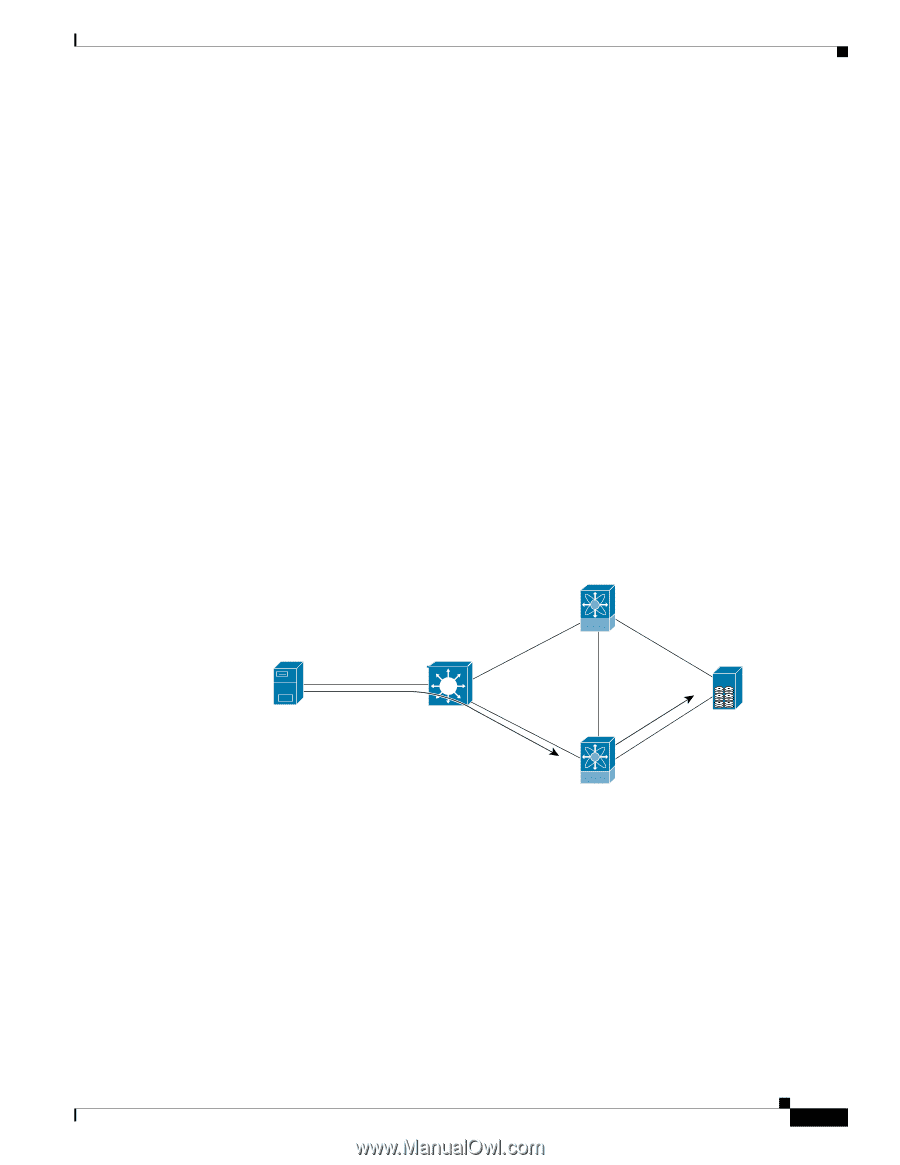
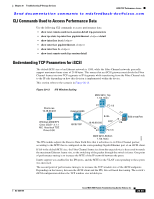
Chapter 20 Troubleshooting IP Storage Services iSCSI TCP Performance Issues Send documentation comments to [email protected] CLI Commands Used to Access Performance Data Use the following CLI commands to access performance data. • show iscsi remote-node iscsi-session-detail tcp-parameters • show ips stats tcp interface gigabitethernet slot/port detail • show interface iscsi slot/port • show interface gigabitethernet slot/port • show interface fc slot/port • show iscsi remote-node fcp-session-detail Understanding TCP Parameters for iSCSI The default MTU size of an Ethernet network is 1500, while the Fibre Channel networks generally support maximum frame sizes of 2148 bytes. This means that an iSCSI gateway must divide the Fibre Channel frames into two TCP segments or IP fragments while transferring from the Fibre Channel side to the IP side depending on how this division is implemented within the device. This section refers to the scenario in Figure 20-13. Figure 20-13 IPS Window Scaling MDS 9216_Top 1.1(0.133c) Shark-nas 10.48.69.233 FC HBA Windows 2000/SP3 Cisco iSCSI - 3.1.1 NIC Alacritech TOE Driver 5.50 2/1 FC 1/3 Catalyst 6000 iSCSI/TCP E-ISL 10.48.69.250 FCP 2/1 FC 1/3 C4 FC ESS 2105/F20 C8 94230 MDS 9216_Bottom 1.1(0.133c) The IPS module adjusts the Receive Data Field Size that it advertises to its Fibre Channel partner, according to the MTU that is configured on the corresponding Gigabit Ethernet port of an iSCSI client. If left to the default MTU size, the Fibre Channel frame size from the target device is decreased to match the maximum Ethernet frame size, so the switching of the packet through the switch is faster. One point of performance tuning is to increase the MTU of the IP network between the peers. Jumbo support was enabled for the IPS ports, and the MTU for the VLAN corresponding to these ports was increased. The second point of performance tuning is to increase the TCP window size of the iSCSI endpoints. Depending on the latency between the iSCSI client and the IPS, this will need fine tuning. The switch's iSCSI configuration defines the TCP window size in kilobytes. OL-9285-05 Cisco MDS 9000 Family Troubleshooting Guide, Release 3.x 20-49