Netgear GS752TS GS7xxTS-TPS Software Admin Manual - Page 114
MAC Based VLAN, Acceptable Frame Type, VLAN Only, Admit All, Ingress Filtering, Enable, Disable
 |
View all Netgear GS752TS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 114 highlights
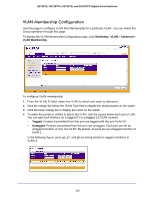
GS728TS, GS728TPS, GS752TS, and GS752TPS Gigabit Smart Switches 3. To configure PVID settings for both physical ports and LAGs, click ALL. 4. Select the check box next to the interfaces to configure. You can select multiple interfaces to apply the same setting to the selected interfaces. Select the check box in the heading row to apply the same settings to all interfaces. 5. Configure the PVID to assign to untagged or priority tagged frames received on this port. The Current PVID field displays the PVID currently configured for the interface. 6. In the Acceptable Frame Type field, specify how you want the port to handle untagged and priority tagged frames. Whichever you select, VLAN tagged frames will be forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN standard. The factory default is Admit All. • VLAN Only: The port will accept only VLAN-tagged frames and will discard any untagged or priority tagged frames it receives. • Admit All: Untagged and priority tagged frames received on the port will be accepted and assigned the value of the Port VLAN ID for this port. 7. In the Ingress Filtering field, specify how you want the port to handle tagged frames: • Enable: A tagged frame will be discarded if this port is not a member of the VLAN identified by the VLAN ID in the tag. In an untagged frame, the VLAN is the Port VLAN ID specified for the port that received this frame. • Disable: All frames are forwarded in accordance with the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN standard. The factory default is Disable. 8. Specify the default 802.1p priority assigned to untagged packets arriving at the port. Possible values are 0-7. 9. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to the latest value of the switch. 10. If you make any changes to this page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes take place immediately. MAC Based VLAN The MAC Based VLAN feature allows incoming untagged frames to be assigned to a VLAN and to classify traffic based on the source MAC address of the frame. A MAC-to-VLAN mapping is defined by configuring an entry in the MAC to VLAN table. An entry is specified via a source MAC address and the desired VLAN ID. The MAC to VLAN configurations are shared across all ports of the device (i.e. there is a system wide table that has MAC address to VLAN ID mappings). When untagged or priority tagged packets arrive at the switch and entries exist in the MAC to VLAN table, the source MAC address of the packet is looked up. If an entry is found, the corresponding VLAN ID is assigned to the packet. If the packet is already priority tagged it will maintain this value; otherwise the priority will be set to zero. The assigned VLAN ID is verified against the VLAN table. If the VLAN is valid, ingress processing on the packet continues; otherwise, the packet is dropped. You can configure a MAC address mapping to a VLAN that has not been created on the system. To access the MAC Based VLAN page, click Switching VLAN Advanced MAC Based VLAN. 114