Netgear GS752TS GS7xxTS-TPS Software Admin Manual - Page 169
Configuring and Viewing Routes, Advertise Lifetime, Preference Level, Cancel, Apply, Routing Table
 |
View all Netgear GS752TS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 169 highlights
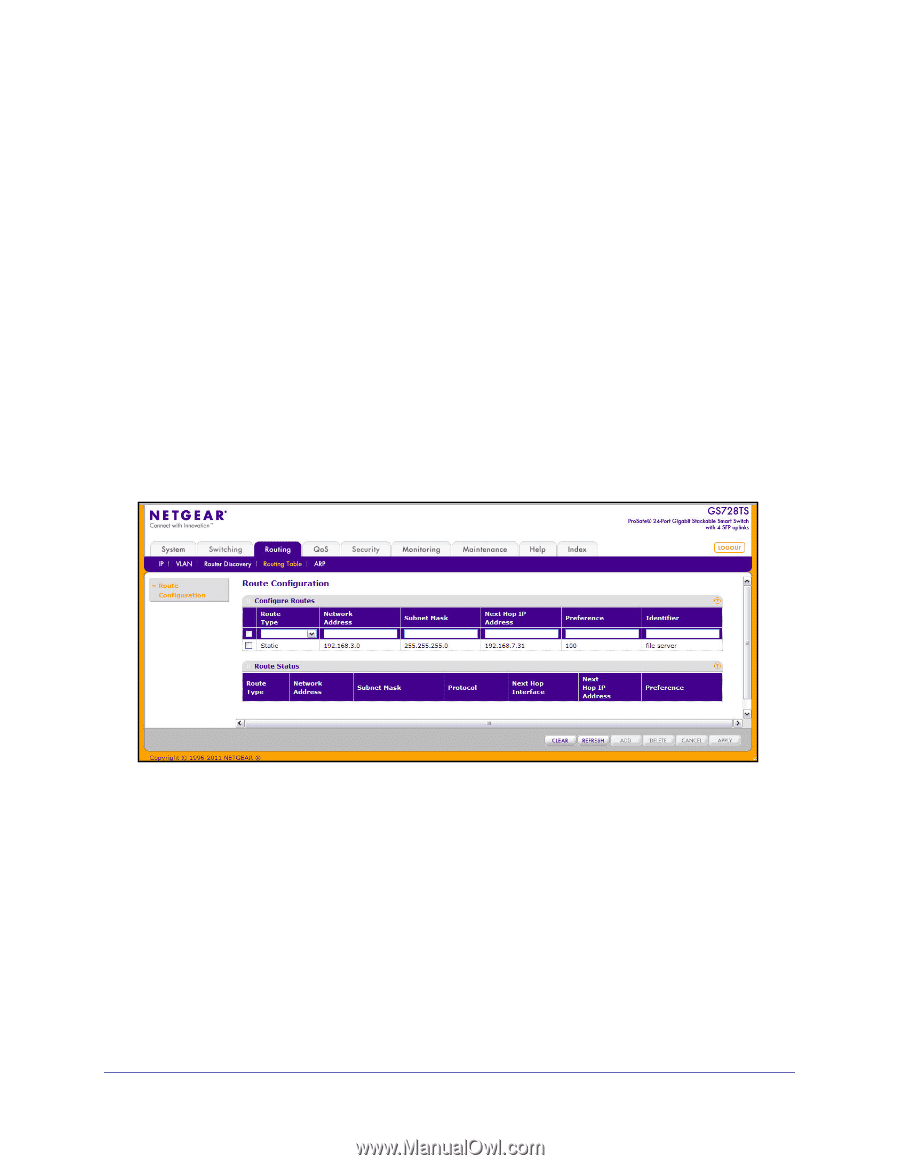
GS728TS, GS728TPS, GS752TS, and GS752TPS Gigabit Smart Switches 6. In the Advertise Lifetime field, enter the value (in seconds) to be used as the lifetime field in router advertisements sent from the interface. This is the maximum length of time that the advertised addresses are to be considered as valid router addresses by hosts. The allowed range for this field is 4 to 9000, i.e., the configured "Maximum Advertise Interval" to 9000. 7. In the Preference Level field, specify the preference level of the router as a default router relative to other routers on the same subnet. Higher numbered addresses are preferred. You must enter an integer. 8. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to the latest value of the switch. 9. If you change any of the settings on the page, click Apply to send the updated configuration to the switch. Configuration changes take effect immediately. Configuring and Viewing Routes From the Routing Table page, you can configure static and default routes and view the routes that the GS728TS, GS728TPS, GS752TS, and GS752TPS has already learned. To display the page click the Routing Routing Table link. To configure a route: 1. In the Route Type field, specify whether the route is to be a Default route or a Static route. If creating a default route, you need to specify only the next hop IP address; otherwise, you need to specify each field. 2. In the Network Address field, specify the IP route prefix for the destination. To create a route, a valid routing interface must exist and the next hop IP Address must be on the same network as the routing interface. 3. In the Subnet Mask field, specify the network mask to indicate the portion of the IP address that identifies the attached network. 4. In the Next Hop IP Address field, specify the outgoing router IP address to use when forwarding traffic to the next router (if any) in the path towards the destination. The next router is always one of the adjacent neighbors or the IP address of the local interface for a 169