Netgear GS752TS GS7xxTS-TPS Software Admin Manual - Page 248
IPv6 ACL, Service Type, Apply, Delete, Cancel, Security, ACL > Advanced
 |
View all Netgear GS752TS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 248 highlights
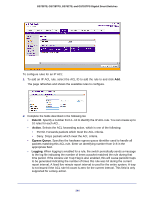
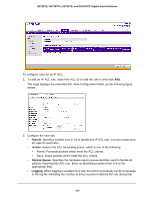
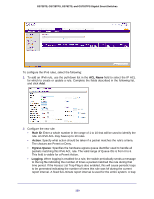
GS728TS, GS728TPS, GS752TS, and GS752TPS Gigabit Smart Switches • Service Type. Choose one of the Service Type match conditions for the extended IP ACL rule. The possible values are IP DSCP, IP precedence, and IP TOS, which are alternative ways of specifying a match criterion for the same Service Type field in the IP header, however each uses a different user notation. After you select the service type, specify the value associated with the type. • IP DSCP: Specify the IP DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) value. The DSCP is defined as the high-order six bits of the Service Type octet in the IP header. Select an IP DSCP value from the menu. To specify a numeric value in the available field, select Other from the menu and type an integer from 0 to 63 in the field. • IP Precedence: The IP Precedence field in a packet is defined as the high-order three bits of the Service Type octet in the IP header. This is an optional configuration. Enter an integer from 0 to 7. • IP TOS Bits: Matches on the Type of Service bits in the IP header when checked. In the first TOS field, specify the two-digit hexadecimal TOS number. The second field is for the TOS Mask, which specifies the bit positions that are used for comparison against the IP TOS field in a packet. The TOS Mask value is a two-digit hexadecimal number from 00 to ff, representing an inverted (i.e. wildcard) mask. The zero-valued bits in the TOS Mask denote the bit positions in the TOS Bits value that are used for comparison against the IP TOS field of a packet. For example, to check for an IP TOS value having bits 7 and 5 set and bit 1 clear, where bit 7 is most significant, use a TOS Bits value of a0 and a TOS Mask of 00. 3. To add the new rule to the ACL, click Apply. 4. To delete a rule from an ACL, select the check box associated with the rule and click Delete. 5. Click Cancel to cancel the configuration on the screen and reset the data on the screen to the latest value of the switch. 6. To modify an existing IP Extended ACL rule, click the Rule ID. The number is a hyperlink to the Extended ACL Rule Configuration page. IPv6 ACL An IPv6 ACL consists of a set of rules which are matched sequentially against a packet. When a packet meets the match criteria of a rule, the specified rule action (Permit/Deny) is taken and the additional rules are not checked for a match. On this menu, the interfaces to which an IP ACL applies must be specified, as well as whether it applies to inbound or outbound traffic. Rules for the IP ACL are specified/created using the IP ACL Rule Configuration menu. To display the IPv6 ACL page, click Security ACL > Advanced IPv6 ACL. 248