HP StorageWorks 8/80 HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 6.1.x administrator guide (5697 - Page 335
Filter-based performance monitoring
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 335 highlights
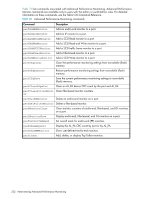
0 0x000024 0x000016 WEB_TOOLS 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 10.106.7.179 1 0x000022 0x000033 WEB_TOOLS 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 10.106.7.179 2 0x000123 0x000789 WEB_TOOLS 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 10.106.7.179 3 0x001212 0x003434 WEB_TOOLS 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 10.106.7.179 switch:admin> perfdeleemonitor 0, 2 End-to-End monitor number 2 deleted switch:admin> Filter-based performance monitoring Filter-based performance monitoring counts the number of times a frame with a particular pattern is transmitted by a port. Filter-based monitoring is achieved by configuring a filter for a particular purpose. The filter can be a standard filter (for example, a SCSI read command filter that counts the number of SCSI read commands that have been transmitted by the port) or a user-defined filter customized for your particular use. For the 4/8 SAN Switch and 4/16 SAN Switch models, the maximum number of filters is 8 per port, in any combination of standard filters and user-defined filters. For the SAN Switch 4/32, 4/64 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 4/32B, 400 Multi-protocol Router, and DC Director models, the maximum number of filters is 12 per port, in any combination of standard filters and user-defined filters. For the 4/256 SAN Director models, the maximum number of filters is 12 per port, in any combination of standard filters and user-defined filters, except for the FC4-48 port blade. For the FC4-48 port blade: • The lower 16 ports (ports 0 through 15) have a maximum of 12 filter monitors per port, and 15 offsets per port for used defined monitors. • The middle 16 port (ports 16 through 31) have a maximum of 6 filter monitors per port, and 11 offsets per port for used defined monitors. • The upper 16 ports (ports 32 through 47) do not support filter monitors. The actual number of filters that can be configured on a port depends on the complexity of the filters. For trunked ports, the filter is configured on the trunk master. You can monitor filter-based performance using the perfMonitorShow command, as described in "Displaying monitor counters" on page 341. You can clear filter-based counters using the perfMonitorClear command, as described in "Clearing monitor counters" on page 344. Adding standard filter-based monitors Table 74 lists the commands for adding standard filter-based monitors to a port. Table 74 Commands to add filter-based monitors Telnet command perfAddReadMonitor perfAddWriteMonitor perfAddRwMonitor perfAddScsiMonitor perfAddIpMonitor Description Count the number of SCSI Read commands Count the number of SCSI Write commands Count the number of SCSI Read and Write commands Count the number of SCSI traffic frames Count the number of IP traffic frames Fabric OS 6.1.x administrator guide 335