HP StorageWorks 8/80 HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 6.1.x administrator guide (5697 - Page 51
Auditable event classes
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 51 highlights
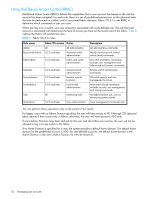
be easily distinguished from other system message log events that occur in the network. Then, at some regular interval of your choosing, you can review the audit events to look for unexpected changes. Before you configure audit event logging, familiarize yourself with the following audit event log behaviors and limitations: • By default, all event classes are configured for audit; to create an audit event log for specific events, you must explicitly set a filter with the class operand and then enable it. • Audited events are generated specific to a switch and have no negative impact on performance. • If you are running Fabric OS versions earlier than 6.x, all Secure Fabric OS events are audited. • Events are not persistently stored on the switch but are streamed to a system message log. • The audit log depends on the system message log facility and IP network to send messages from the switch to a remote host. Because the audit event log configuration has no control over these facilities, audit events can be lost if the system message log and IP network facilities fail. • If too many events are generated by the switch, the system message log will become a bottleneck and audit events will be dropped by the Fabric OS. • If the user name, IP address, or user interface is not transported, an audit message is logged by adding the message None to each of the respective fields. • For High Availability, the audit event logs exist independently on both active and standby CPs. The configuration changes that occur on the active CP are propagated to the standby CP and take effect. • Audit log configuration is updated through a configuration download. See the Fabric OS Command Reference for more information about the auditCfg command and command syntax. Auditable event classes You configure the audit log using the auditCfg command. Before configuring an audit log, you must select the event classes you want audited. When enabled, the audit log feature audits any RASLog messages (system message log) previously tagged as AUDIT in Fabric OS 6.x. The audit log includes: • SEC-3001 through SEC-3017 • SEC-3024 through SEC-3029 • ZONE-3001 through ZONE-3012 Table 5 identifies auditable event classes and auditCfg operands used to enable auditing of a specific class. Table 5 AuditCfg event class operands Operand Event class Description 1 Zone Audit zone event configuration changes, but not the actual values that were changed. For example, a message may state, "Zone configuration has changed," but the syslog does not display the actual values that were changed. 2 Security Audit any user-initiated security events for all management interfaces. For events that have an impact on an entire fabric, an audit is generated only for the switch from which the event was initiated. 3 Configuration Audit configuration downloads of existing SNMP configuration parameters. Configuration uploads are not audited. 4 Firmware Audit firmware download start, firmware complete, and any other errors encountered during a firmware download. 5 Fabric Audit administrative domain-related changes. Fabric OS 6.1.x administrator guide 51