HP StorageWorks 8/80 HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 6.2 administrator guide (5697-0 - Page 341
Optimizing fabric behavior
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 341 highlights
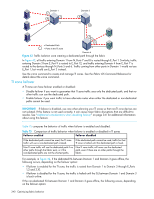
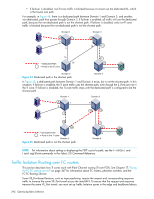
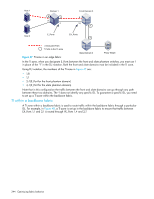
16 Optimizing fabric behavior Adaptive Networking overview Adaptive Networking is a suite of tools and capabilities that enable you to ensure optimized behavior in the SAN. Even under the worst congestion conditions, the Adaptive Networking features can maximize the fabric behavior and provide necessary bandwidth for high-priority, mission-critical applications and connections. The Top Talkers feature provides real-time information about the top n bandwidth-consuming flows from a set of a large number of flows passing through a specific port in the network. You can use Top Talkers to identify the SID/DID pairs that consume the most bandwidth and can then configure them with certain QoS attributes so they get proper priority. The Top Talkers feature is part of the licensed Advanced Performance Monitoring feature. See "Top Talker monitors" on page 414 for detailed information about Top Talkers. The following sections cover three features in the Adaptive Networking suite: • Traffic Isolation Routing • QoS Ingress Rate Limiting • QoS SID/DID Traffic Prioritization Top Talkers, which is another Adaptive Networking feature, is described briefly in this chapter and described in detail in Chapter 18, "Administering advanced performance monitoring" on page 405. Traffic Isolation Routing The Traffic Isolation Routing feature allows you to control the flow of interswitch traffic by creating a dedicated path for traffic flowing from a specific set of source ports (N_Ports). For example, you might use Traffic Isolation Routing for the following scenarios: • To dedicate an ISL to high priority, host-to-target traffic. • To force high volume, low priority traffic onto a given ISL to limit the effect on the fabric of this high traffic pattern. • To ensure that requests and responses of FCIP-based applications such as tape pipelining use the same VE_Port tunnel across a metaSAN. Traffic isolation is implemented using a special zone, called a Traffic Isolation zone (TI zone). A TI zone indicates the set of N_Ports and E_Ports to be used for a specific traffic flow. When a TI zone is activated, the fabric attempts to isolate all inter-switch traffic entering from a member of the zone only to those E_Ports that have been included in the zone. The fabric also attempts to exclude traffic not in the TI zone from using E_Ports within that TI zone. Figure 42 shows a fabric with a TI zone consisting of the following ports: • N_Ports:1,7, 1,8, 4,5, and 4,6 • E_Ports:1,1, 3,9, 3,12, and 4,7 The dashed line indicates the dedicated path from Domain 1 to Domain 4. Fabric OS 6.2 administrator guide 339