HP StorageWorks 8/80 HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 6.2 administrator guide (5697-0 - Page 397
How LSAN zone binding works
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 397 highlights
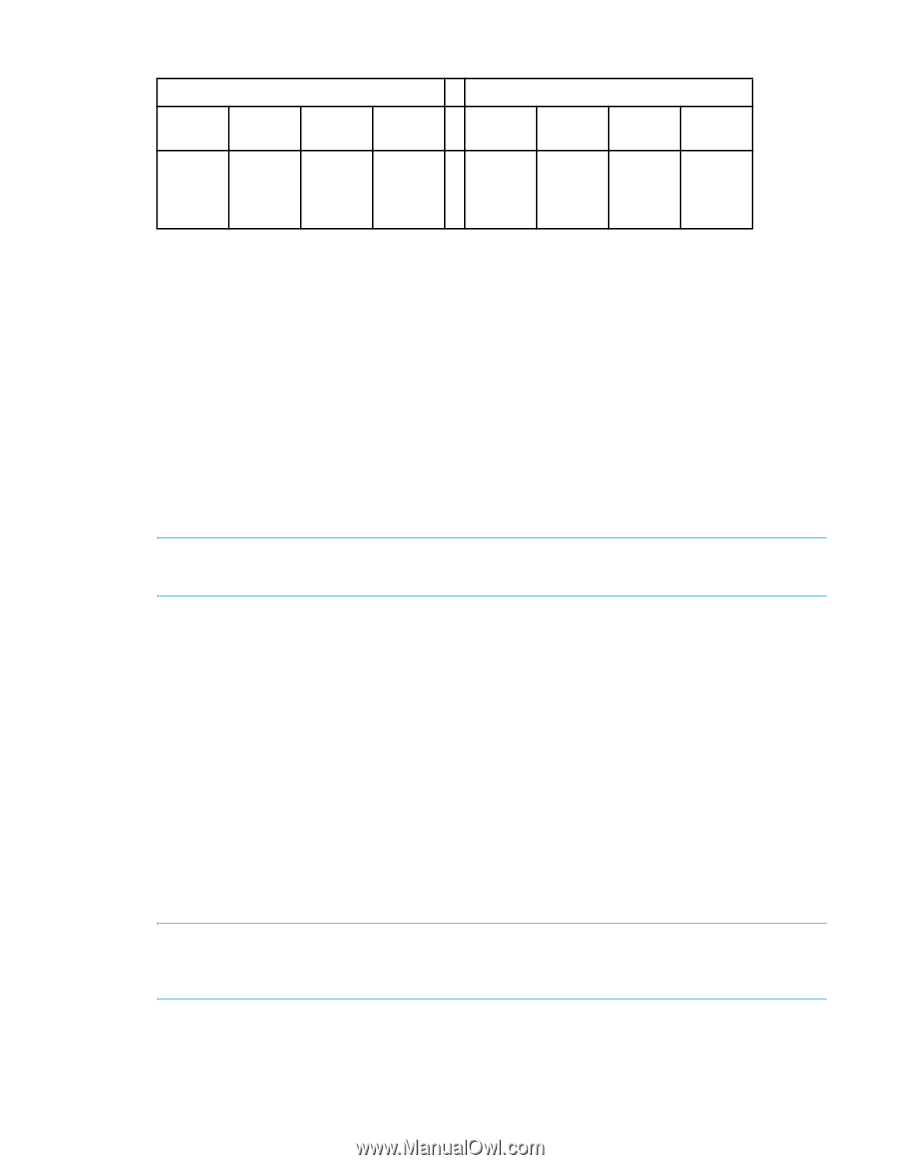
Table 77 LSAN information stored in each FC router with and without LSAN zone binding WIthout LSAN zone binding With LSAN zone binding FC FC FC FC router 1 router 2 router 3 router 4 FC FC FC FC router 1 router 2 router 3 router 4 LSAN 1 LSAN 2 LSAN 3 LSAN 4 LSAN 1 LSAN 2 LSAN 3 LSAN 4 LSAN 1 LSAN 2 LSAN 3 LSAN 4 LSAN 1 LSAN 2 LSAN 3 LSAN 4 LSAN 1 LSAN 2 LSAN 2 LSAN 3 LSAN 4 LSAN 4 To summarize: • Without LSAN zone binding, the maximum number of LSAN devices is 10,000. • With LSAN zone binding, the metaSAN can import more than 10,000 devices and the backbone fabric can support more FC routers. • With LSAN zone binding, CPU consumption by an FC router is lower. How LSAN zone binding works LSAN zone binding uses an FC router matrix, which specifies pairs of FC routers in the backbone fabric that can access each other, and an LSAN fabric matrix, which specifies pairs of edge fabrics that can access each other. You set up LSAN zone binding using the fcrLsanMatrix command. This command has two options: -fcr and -lsan. The -fcr option is for creating and updating the FC router matrix, and the -lsan option is used for creating and updating the LSAN fabric matrix. See the Fabric OS Command Reference for a complete description of this command. NOTE: As a best practice, use this feature in a backbone fabric in which all FC routers are running Fabric OS 6.1.0 or later. When you set up LSAN zone binding on the local FC router running Fabric OS 6.1.0 or later, the resulting matrix database is automatically distributed to all of the 6.1.0 or later FC routers in the backbone fabric. You do not need to set up LSAN zone binding on the other FC routers unless those FC routers are running Fabric OS versions earlier than 6.1.0. If a new FC router joins the backbone fabric, the matrix database is automatically distributed to that FC router. For FC routers running a Fabric OS version earlier than 6.1.0: • The matrix database is not automatically distributed from this FC router to other FC routers. • You must manually configure the LSAN fabric matrix on these FC routers to match the other FC routers in the backbone fabric. If you have a dual backbone configuration, where two backbone fabrics share edge fabrics, the LSAN fabric matrix and FC router matrix settings for the shared edge fabrics must be the same on both backbone fabrics. The matrix databases are not automatically propagated from one backbone fabric to another, so you must make sure that both backbone fabrics have the same matrix settings. NOTE: You can use LSAN zone binding along with the LSAN tagging to achieve better scalability and performance. See "LSAN zone policies using LSAN tagging" on page 390 for information about using the Enforce LSAN tag. Fabric OS 6.2 administrator guide 395