HP StorageWorks 8/80 HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 6.2 administrator guide (5697-0 - Page 428
Fibre Channel Frame fields, Field size, Total
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 8/80 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 428 highlights
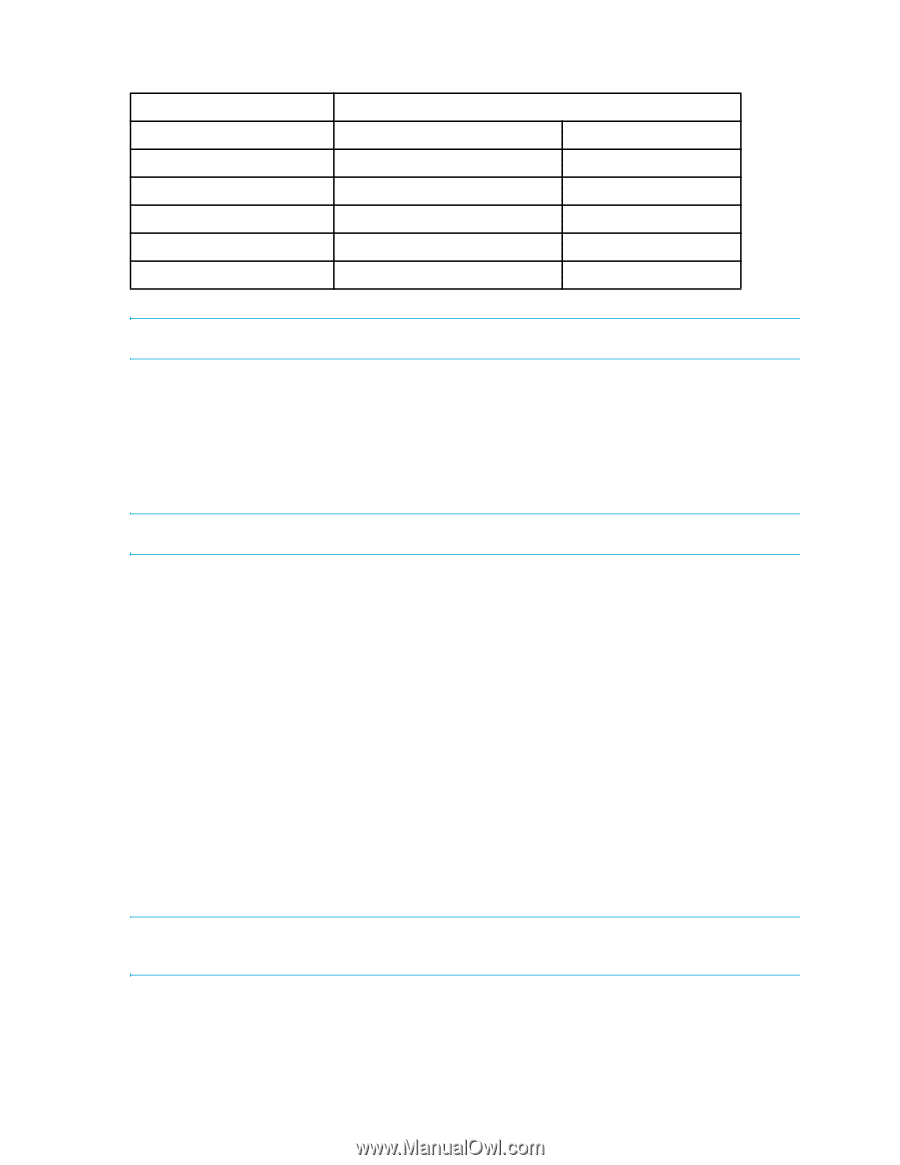
The following table describes Fibre Channel data frames. Table 81 Fibre Channel data frames Fibre Channel Frame fields Field size Start of frame 4 bytes 32 bits Standard frame header 24 bytes 192 bits Data (payload) 0-2112 bytes 0-16,896 bits CRC 4 bytes 32 bits End of frame 4 bytes 32 bits Total (Number bits/frame) 36-2148 bytes 288-17,184 bits NOTE: The term byte used in Table 81 equals 8 bits. The maximum Fibre Channel frame is 2148 bytes. You can allocate buffer credit using the portCfgLongDistance command, which allows you to allocate sufficient numbers of full-size frame buffers on a particular port or to support a long- distance link. Only E_Ports can be configured for extended distances. Changes made by this command are persistent across switch reboots and power cycles. Enter the portCfgLongDistance command to select one of the following four options for buffer credit allocation: NOTE: Long distance modes L0.5, L1, and L2 are not supported on Fabric OS 6.x. • Level 0 static mode (L0)-L0 is the normal (default) mode for a port. Each user port reserves eight buffer credits and competes with other ports for additional buffer credits. No buffer credits are reserved for extended distance ISLs. • Level E static mode (LE)-LE reserves a static number of buffer credits, which supports distances up to 10 km. The number reserved depends on the port speed. The baseline for the calculation is one credit per km at 2 Gb/s. This yields the following values for 10 km: • 5 credits per port at 1 Gb/s • 10 credits per port at 2 Gb/s • 20 credits per port at 4 Gb/s • 40 credits per port at 8 Gb/s • Dynamic Mode (LD)-LD calculates buffer credits based on the distance measured during port initialization. An upper limit is placed on the calculation by providing a desired distance value. If the measured distance is more than desired distance, the desired distance is used in the calculation; otherwise, the measured distance is used. This is a mechanism for controlling the number of reserved buffer credits ensure buffer availability for other ports in the same group. • Static long-distance mode (LS)-LS calculates a fixed number of buffer credits based on a desired distance value. NOTE: For the LD and LS distance levels, see "Determining how many ports can be used for long distance" on page 425 to get an approximation of the calculated number of buffer credits. 424 Administering extended fabrics