VMware VLM3-ENG-CP User Guide - Page 176
Processor Type Incompatibility, Viewing Virtual Switches for Fences
 |
View all VMware VLM3-ENG-CP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 176 highlights
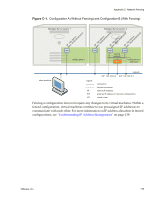
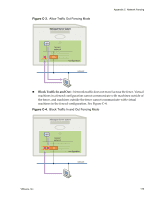
VMware® Lab Manager User's Guide This option is useful in these circumstances: „ You are testing software viruses that need to remain isolated from the network. „ You are testing a client‐server application in isolation. Processor Type Incompatibility Deploying a configuration in fenced mode hosts all the virtual machines on a single Managed Server system. You must have a Managed Server system connected to the storage server where the templates that serve as the basis of this configuration reside on. The Managed Server system must have sufficient resources, such as memory, slots, and fences. If you deploy a configuration, perform an operation which saves the state of the configuration (for example, suspend or capture to library), and redeploy the configuration with fencing (which requires hosting all virtual machines on the same physical machine), a situation could come up where the only Managed Server systems available are ones with incompatible processor types. The captured memory expects a particular processor type. To address this situation, deploy the configuration without fencing, undeploy it without saving the memory state (use the Turn Off deployment setting in the User Preferences page or the Undeploy ‐ Discard State mouseover menu), and redeploy the configuration. If deploying a configuration without fencing is not an option, reset the MAC address of each virtual machine to remove the saved state, and redeploy the configuration. See "Changing IP or MAC Addresses" on page 34. Viewing Virtual Switches for Fences You can use the VI Client in the ESX Server system to see the "LMNetwork" virtual switches or networks that Lab Manager creates for each fence. To view virtual switches for fences 1 Navigate to the Configuration tab of the VI Client. 2 Click the Networking link in the Hardware list to view virtual switches (for example, "LMNetwork001"). See the VMware Infrastructure 3 documentation for details on using VI Client. 176 VMware, Inc.