Intel 925 Data Sheet - Page 177
DRAM Technologies and Organization
 |
UPC - 683728067724
View all Intel 925 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 177 highlights
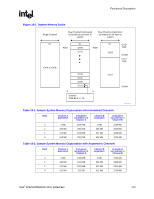
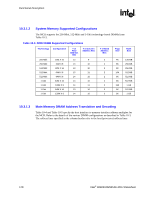
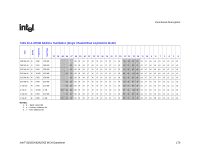
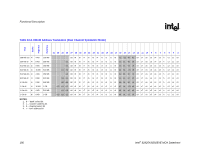
Functional Description R 10.3.1 10.3.1.1 DRAM Technologies and Organization All standard 256-Mb, 512-Mb, and 1-Gb technologies and addressing are supported for x16 and x8 devices. • All supported DDR2 devices have 4 or 8 banks. • The MCH supports various page sizes. Page size is individually selected for every rank. • 4 KB, 8 KB, and 16 KB for asymmetric, interleaved, or single channel modes. • The DRAM sub-system supports single or dual channels, 64b wide per channel for non-ECC and 72b wide per channel with ECC (82925X MCH only). • There can be a maximum of 4 ranks populated (2 Double Sided DIMMs) per channel. • Mixed mode Double Sided DIMMs (x8 and x16 on the same DIMM) are not supported • By using 1-Gb technology, the largest memory capacity is 8 GB 32M rows/bank * 4 banks/device * 8 columns * 8 devices/rank * 4 ranks/channel * 2 channel * 1b/(row*column) * 1G/1024M * 1B/8b = 8 GB. Though it is possible to put 8 GB in system by stuffing both channels this way, the MCH is still limited to 4 GB of addressable space due to the number of address pins on the FSB. • By using 256Mb technology, the smallest memory capacity is 128 MB (4M rows/bank * 4banks/device * 16 columns * 4 devices/rank * 1 rank * 1B/8b =128 MB) • DDR2 533 with CAS latency timings of 3-3-3, unbuffered non-ECC x8 DIMMS are supported at 1.9 V. Rules for Populating DIMM Slots • In all modes, the frequency of system memory will be the lowest frequency of all DIMMs in the system, as determined through the SPD registers on the DIMMs. • In the Single Channel mode, any DIMM slot within the channel may be populated in any order. Either channel may be used. To save power, do not populate the unused channel. • In Dual Channel Asymmetric mode, any DIMM slot may be populated in any order. • In Dual Channel Interleaved mode, any DIMM slot may be populated in any order, but the total memory in each channel must be the same. Intel® 82925X/82925XE MCH Datasheet 177