Intel 925 Data Sheet - Page 19
System Interrupts - pentium d
 |
UPC - 683728067724
View all Intel 925 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
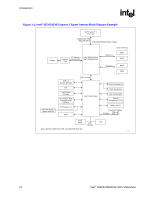
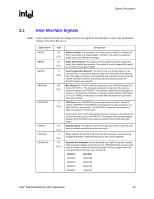
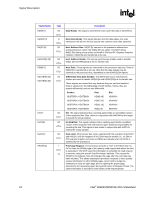
Introduction R 1.3.5 Features of the PCI Express Interface include: • One x16 PCI Express port intended for graphics attach, compatible with the PCI Express Base Specification revision 1.0a. • Theoretical PCI Express transfer rate of 2.5 Gb/s. • Raw bit-rate on the data pins of 2.5 Gb/s, resulting in a real bandwidth per pair of 250 MB/s given the 8b/10b encoding used to transmit data across this interface • Maximum theoretical realized bandwidth on the interface of 4 GB/s in each direction simultaneously, for an aggregate of 8 GB/s when (1)x16. • PCI Express Graphics Extended Configuration Space. The first 256 bytes of configuration space alias directly to the PCI Compatibility configuration space. The remaining portion of the fixed 4-KB block of memory-mapped space above that (starting at 100h) is known as extended configuration space. • PCI Express Enhanced Addressing Mechanism. Accessing the device configuration space in a flat memory mapped fashion. • Automatic discovery, negotiation, and training of link out of reset • Supports traditional PCI style traffic (asynchronous snooped, PCI ordering) • Supports traditional AGP style traffic (asynchronous non-snooped, PCI Express-relaxed ordering) • Hierarchical PCI-compliant configuration mechanism for downstream devices (i.e., normal PCI 2.3 Configuration space as a PCI-to-PCI bridge) • Supports "static" lane numbering reversal. This method of lane reversal is controlled by a Hardware Reset strap, and reverses both the receivers and transmitters for all lanes (e.g., TX15->TX0, RX15->RX0). This method is transparent to all external devices and is different than lane reversal as defined in the PCI Express Specification. In particular, link initialization is not affected by static lane reversal. System Interrupts The MCH interrupt support includes: • Supports both 8259 and Pentium 4 processor FSB interrupt delivery mechanisms. • Supports interrupts signaled as upstream Memory Writes from PCI Express and DMI ⎯ MSIs routed directly to FSB ⎯ From I/OxAPICs Intel® 82925X/82925XE MCH Datasheet 19