VMware 4817V62 Administration Guide - Page 238
Datastore Condition and State Triggers, Event Triggers
 |
View all VMware 4817V62 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 238 highlights
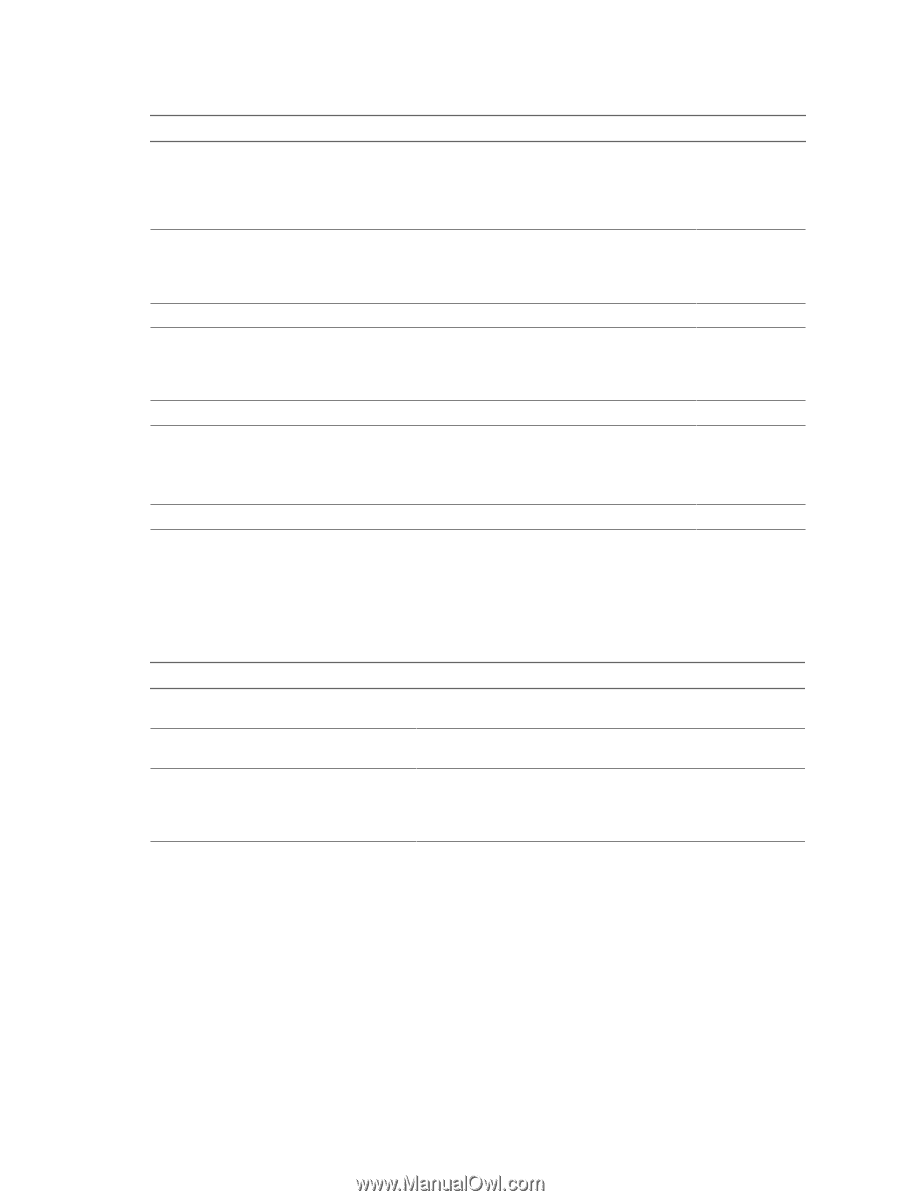
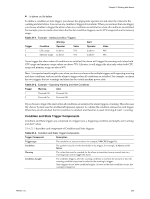
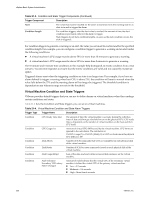
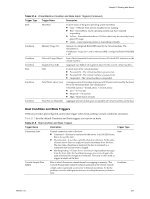
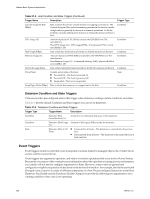
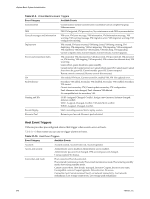
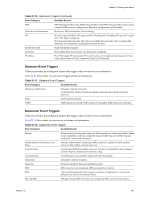
vSphere Basic System Administration Table 21-5. Host Condition and State Triggers (Continued) Trigger Name Description Trigger Type Console SwapOut Rate (KBps) Rate at which the service console kernel is swapping out memory. The Console Swapout Rate indicates memory pressure in the service console. A high value is generally a precursor to timeout operations. To fix the problem, consider adding more memory or ending the memory-intensive task. Condition CPU Usage (%) Amount of physical CPU (MHz) used by the ESX/ESXi host. The calculation is: Host CPU Usage (%) = CPU usage [MHz] / (# of physical CPUs x clock rate [MHz]) x 100 Condition Disk Usage (KBps) Sum of the data read from and written to all disk instances on the host. Condition Memory Usage (%) Amount of physical RAM (MB) consumed by the ESX/ESXi host. The calculation is: Host Memory Usage (%) = Consumed Memory [MB] / physical RAM of server [MB] x 100 Condition Network Usage (kbps) Sum of data transmitted and received for all the NIC instances of the host. Condition Power State Current power state of the host: n Powered On - The host is powered on. n Powered Off - The host is powered off. n Suspended - The host is suspended. State Swap Pages Write (KBps) Rate at which host memory is swapped out to the disk. Condition Datastore Condition and State Triggers VMware provides preconfigured alarms that trigger when datastores undergo certain conditions and states. Table 21-6 lists the default Condition and State triggers you can set on datastores. Table 21-6. Datastore Condition and State Triggers Trigger Type Trigger Name Description Condition Condition State Datastore Disk Overallocation (%) Amount of overallocated disk space in the datastore. Datastore Disk Usage Amount of disk space (KB) used by the datastore. (%) Datastore State to All Hosts n Connected to all hosts - The datastore is connected to at least one host. n Disconnected from all hosts - The datastore is disconnected from at least one host. Event Triggers Event triggers monitor events that occur in response to actions related to managed objects, the vCenter Server system, and the License Server. Event triggers use arguments, operators, and values to monitor operations that occur in the vServer System. Because the occurrance of the event gives you information about the operation occurring in your environment, you usually will not need to configure arguments for them. However, some events are general and configuration might be required to set the alarm on the desired information. For example, the Hardware Health Changed event occurs for a variety of different subsystems on a host.The preconfigured datacenter alarm Host Hardware Fan Health uses the Hardware Health Changed event with the following two arguments to set a warning condition when a fan is not operating: 238 VMware, Inc.