VMware 4817V62 Administration Guide - Page 341
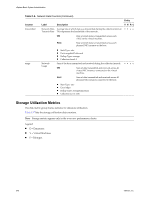
If Memory Swap Target is greater than Memory Swap, then
 |
View all VMware 4817V62 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 341 highlights
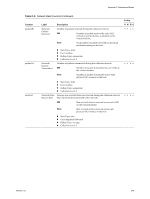
Appendix C Performance Metrics Table C-5. Memory Data Counters (Continued) Entity Counter Label Description VHR C swapout Memory Swap Out Amount of memory that has been swapped out to disk. VM Total amount of memory data that has been written out to the virtual machine's swap file from machine memory by the VMkernel. This statistic refers to VMkernel swapping and not to guest OS swapping. Host Sum of Memory Swap Out of all powered on VMs on the host. ••ο ο swapoutRate swapped swaptarget Memory Swap Out Rate Memory Swapped Memory Swap Target n Stats Type: absolute n Unit: kiloBytes n Rollup Type: average (min/max) n Collection Level: 2(4) Rate at which memory is being swapped from active memory to disk during the current interval. This counter applies to virtual machines and is generally more useful than the swapout counter to determine if the virtual machine is running slow due to swapping, especially when looking at real-time statistics. n Stats Type: rate n Unit: kiloBytesPerSecond n Rollup Type: average (min/max) n Collection Level: 1(4) ••ο ο Current amount of guest physical memory swapped out to the virtual machine's swap file by the VMkernel. Swapped memory stays on disk until the virtual machine needs it. This statistic refers to VMkernel swapping and not to guest OS swapping. swapped = swapin +swapout n Stats Type: absolute n Unit: kiloBytes n Rollup Type: average (min/max) n Collection Level: 2(4) Amount of memory available for swapping. •ο ο ο Target value for the virtual machine swap size, as determined by the VMkernel. The VMkernel sets a target for the level of swapping for each virtual machine, based on a number of factors. If Memory Swap Target is greater than Memory Swap, then the VMkernel will start swapping, causing more virtual machine memory to be swapped out. This will generally happen quickly. If Memory Swap Target is less than Memory Swap, then the VMkernel will stop swapping. Since swapped memory stays swapped until the virtual machine accesses it, Memory Swapped can be greater than Memory Swap Target, possibly for a prolonged period of time. This simply means that the swapped memory is not currently needed by the virtual machine and is not a cause for concern. n Stats Type: absolute n Unit: kiloBytes n Rollup Type: average (min/max) n Collection Level: 2(4) VMware, Inc. 341