VMware 4817V62 Administration Guide - Page 68
Con Syslog on ESXi Hosts, Export Diagnostic Data, Configuration, Advanced Settings, Syslog
 |
View all VMware 4817V62 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 68 highlights
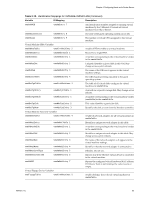
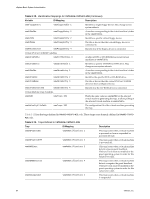
vSphere Basic System Administration Configure Syslog on ESXi Hosts All ESX/ESXi hosts run a syslog service (syslogd), which logs messages from the VMkernel and other system components to a file. On an ESXi host, you can use the vSphere Client or the vSphere CLI command vicfg-syslog to configure the following options: Log file path Remote host Remote port Specifies a datastore path to a file in which syslogd logs all messages. Specifies a remote host to which syslog messages are forwarded. In order to receive the forwarded syslog messages, your remote host must have a syslog service installed and correctly configured. Consult the documentation for the syslog service installed on your remote host for information on configuration. Specifies the port on which the remote host receives syslog messages. You cannot use the vSphere Client or vicfg-syslog to configure syslog behavior for an ESX host. To configure syslog for an ESX host, you must edit the /etc/syslog.conf file. For more information on vicfg-syslog, see the vSphere Command-Line Interface Installation and Reference Guide. Procedure 1 In the vSphere Client inventory, select the host. 2 Click the Configuration tab. 3 Click Advanced Settings. 4 Select Syslog in the tree control. 5 In the Syslog.Local.DatastorePath text box, enter the datastore path for the file to which syslog will log messages. The datastore path should be of the form [] , where the path is relative to the root of the volume backing the datastore. For example, the datastore path [storage1] var/log/messages would map to the path /vmfs/volumes/storage1/var/log/messages. If no path is specified, the default path is /var/log/messages. 6 In the Syslog.Remote.Hostname text box, enter the name of the remote host to which syslog data will be forwarded. If no value is specified, no data is forwarded. 7 In the Syslog.Remote.Port text box, enter the port on the remote host to which syslog data will be forwarded. By default, this option is set to 514, which is the default UDP port used by syslog. Changes to this option take effect only if Syslog.Remote.Hostname is configured. 8 Click OK. Changes to the syslog options take effect immediately. Export Diagnostic Data You can export all or part of your log file data. When you export log file data, the vm-support script creates a file of the selected data and stores it in a location you specify. The default file type is .txt if no other extension is specified. The file contains Type, Time, and Description. 68 VMware, Inc.